The stevia plant (Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni) contains several steviol glycosides (structures see also publication: Stevia im Visier) which are known for their sweetening power. Rebaudioside A (E960) and stevioside are approved for use with food in Europe since december 2011. In the meantime rebaudioside A is included in several sweeteners. Besides the two approved sweeteners the extracts of the plant consist of additional steviol glycosides, many amino acids, proteins and carbohydrates. Generally the analysis of steviol glycosides is a challenge, because on the one hand detectability is difficult and on the other hand the substances are uncharged. Therefore the UV detection is made at a low range and ionisation is imposed due to formation of complexes with borate. Using an electrolyte with gel the separation of the known steviol glycosides is possible.
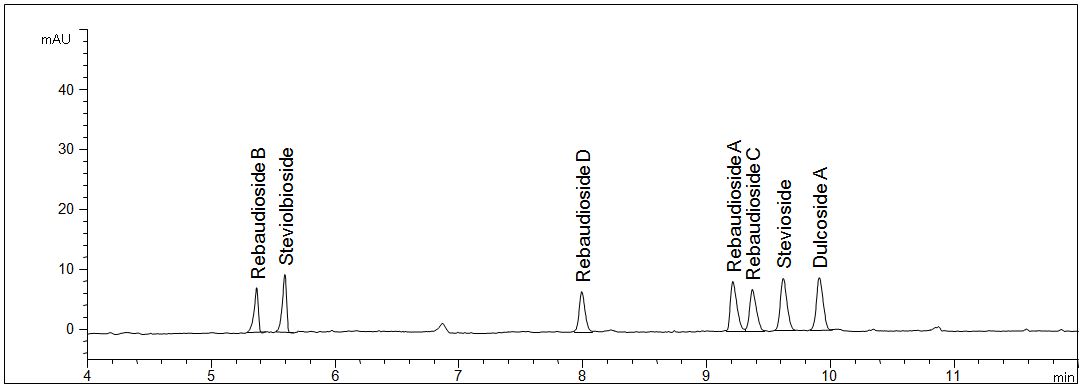
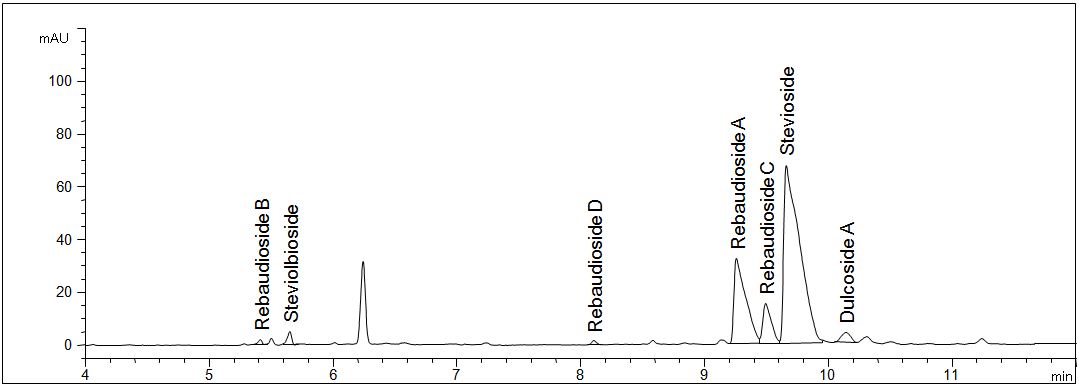
Standard solution steviolglycosides
- Separation: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The standard solution contains the seven most important steviol glycosides in a concentration of 20 mg/l each.
Download: Stevia_1.pdf
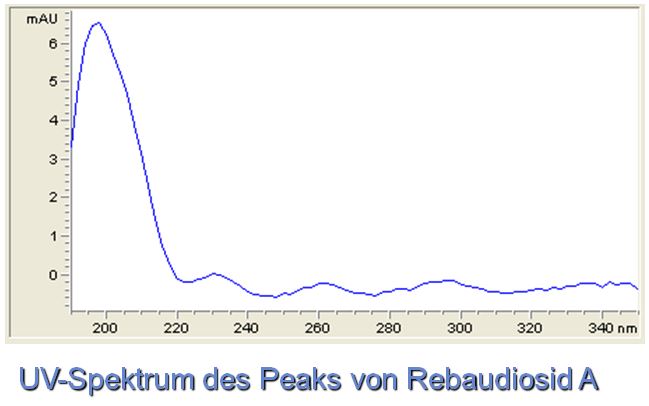
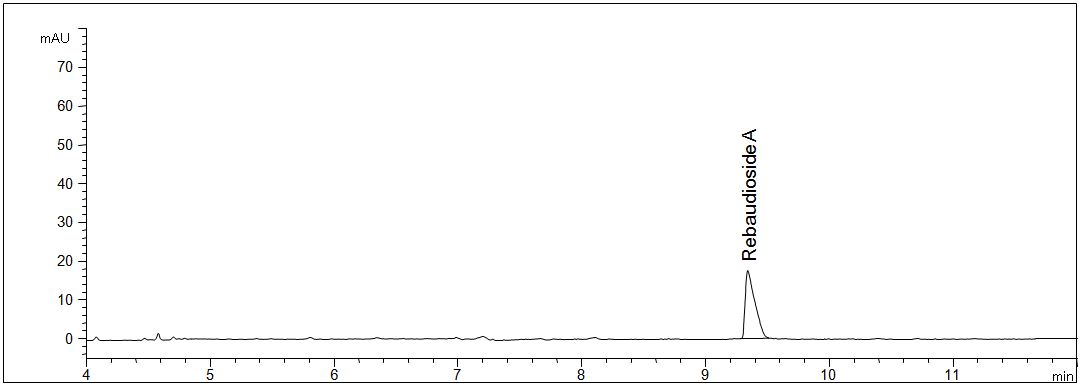
UV-Spektra and 3D-view
- Separatin: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The figures show the 3D spectrum oft he separated sample solution as well as the spectrum of rebaudioside A. The spectral data of the other steviol glycosides are nearly identical.
Download: Stevia_2.pdf
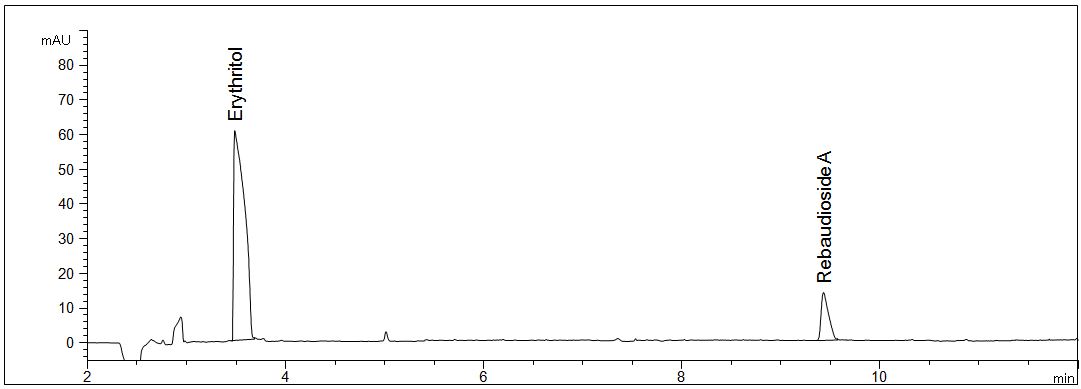
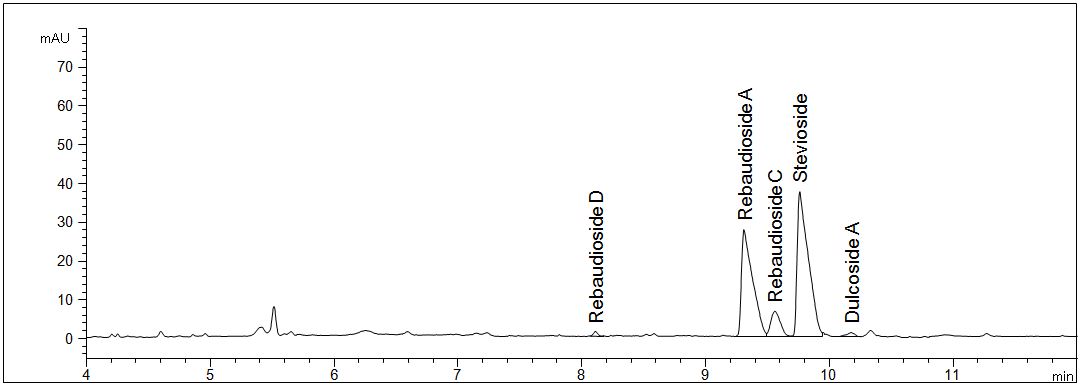
Erythritol and rebaudioside A in stevia sticks
-
- Spearation: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- • Description: The sample weigth of the sweetener is 10000 mg/l. The sugar alcohol erythritol and rebaudioside A can be analysed simultaneously.
Download: Stevia_3.pdf
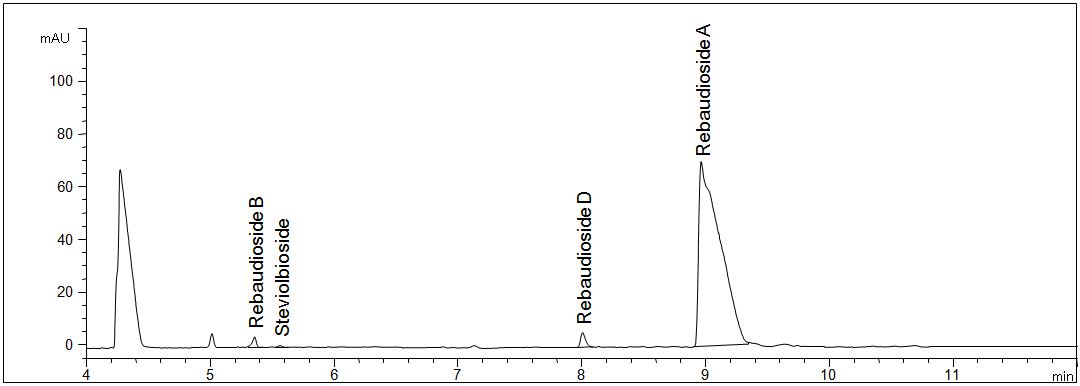
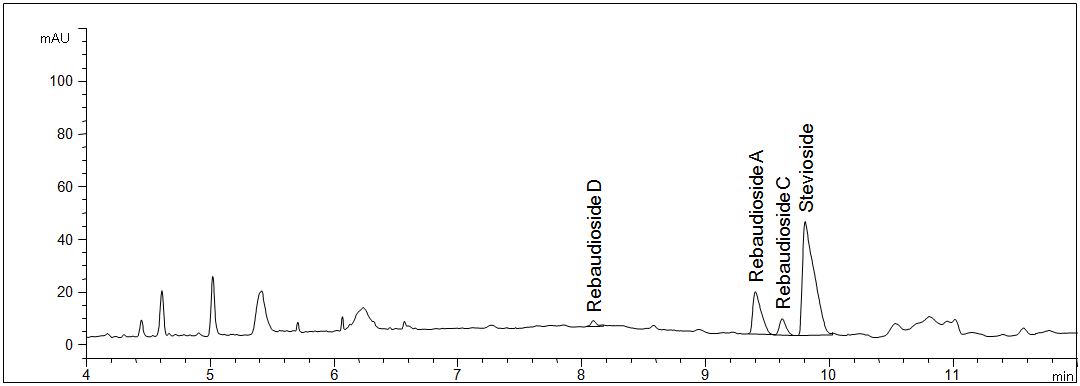
Dried leaves of stevia
- Separation: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The leaves were extracted in hot pure water.
Download: Stevia_4.pdf
Alcoholic extract of stevia
- Separation: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The extract was 1:100 diluted with pure water.
Download: Stevia_5.pdf
Aqueous extract of stevia
- Separation: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The extract was 1:100 diluted with pure water.
Download: Stevia_6.pdf
Stevia powder
- Separationk: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The sample weight was 2000 mg/l.
Download: Stevia_7.pdf
Stevia in tablets
- Separation: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The sample weight was about 50 mg in 20 ml pure water.
Download: Stevia_8.pdf
Fresh leaves of stevia
- Separation: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: About 200 mg leaves were extracted in hot pure water.
Download: Stevia_9.pdf
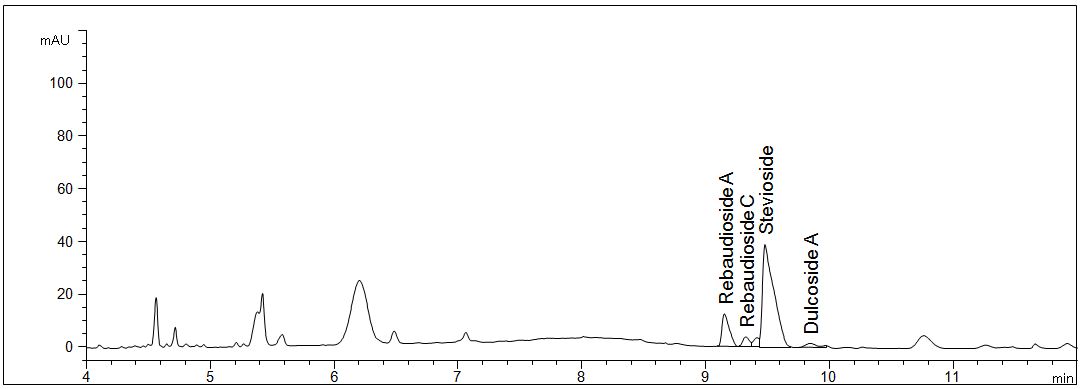
Analysis of blossoms, leaves and stems of the stevia plant
- Separation: CGE
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS-HPMC
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The respective parts of the pureed plant were weigthed and extracted with cold pure water. Steviol glycosides are detectable in each part of the plant. Furthermore additional peaks are visible, presumably amino acids, proteins and carbohydrates.
Download: Stevia_10.pdf