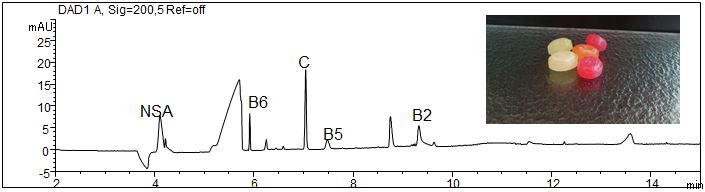
Water-soluble vitamins can be baseline-separated with micellar electrokinetic chromatography with good resolution of the substances. The application of micelles is necessary to mobilize nicotinic acid amide and vitamin B12 (hydroxycobalamin) and to separate them from the EOF. As most of the water-soluble vitamins show very characteristic UV-spectra the assignment of the substances in difficult samples can be done due to their migration time and their UV-spectra, respectively.
Using the short part of the capillary a fast screening of the water-soluble vitamins can be achieved in less than three minutes (short end).
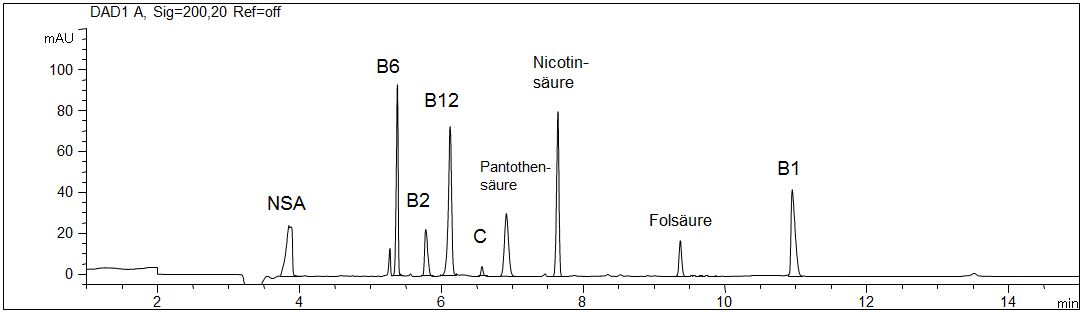
Standard solution of vitamins
- Separation: MEKC
- Electrolyt: Borate-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The standard solution contains nine water-soluble vitamins in a concentration of 20 mg/l each (pantothenic acid and ascorbic acid 40 mg/l each).
Download: Vitamine_1.pdf
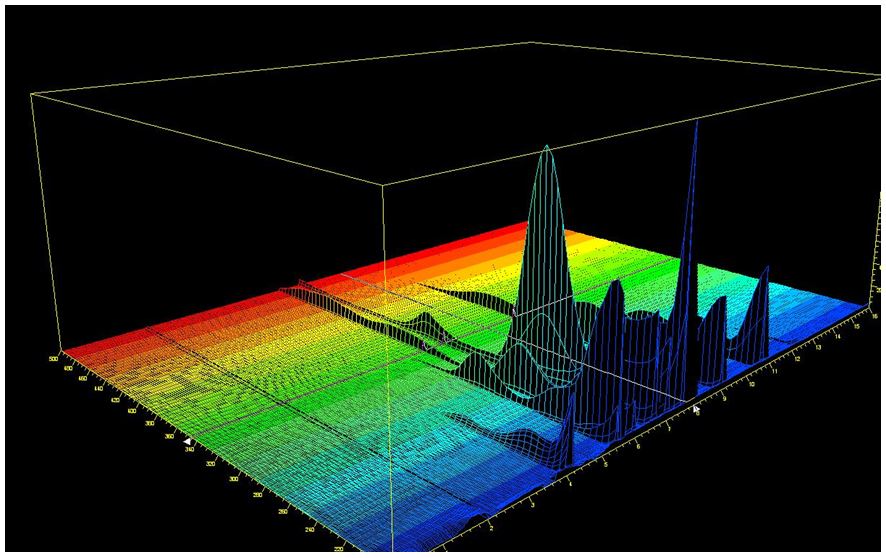
3D presentation of spectra of the vitamins
- Separation: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The 3D plot of the standard solution shows the great variety of the UV-spectra of the vitamins. For example for ascorbic acid a maximum is found at about 270 nm.
Download: Vitamine_2.pdf
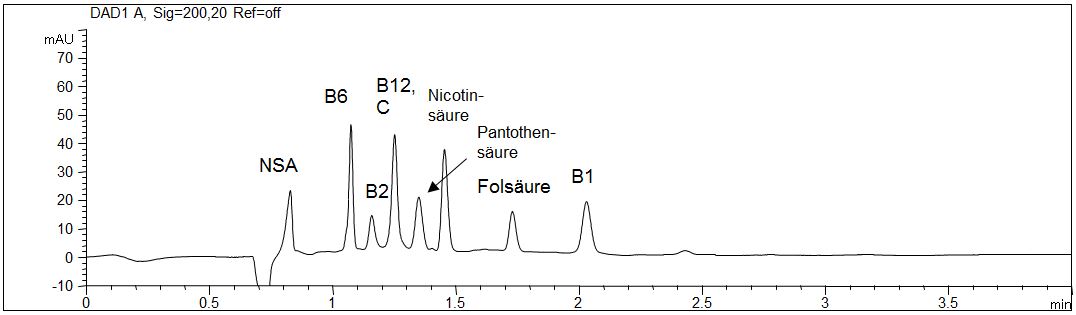
Fast determination of vitamines: short end injection
- Separation: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, effective length 8 cm
- Injection: 5 s, -50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: A fast screening of the sample is possible when the injection is done form the side of the detector. In some part a decrease in resolution is observed.
Download: Vitamine_3.pdf
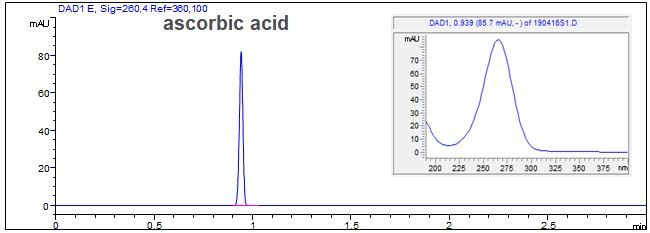
Determination of vitamin C (ascorbic acid): Short end injection
Vitamin C
Vitamins are organic molecules that are essential for organisms for the proper function of its metabolic processes. The most prominent vitamin is vitamin C, also called ascorbic acid, which is a water soluble vitamin. It protects the cells from free radicals. Because vitamin C is not stored, daily intake is necessary. Good sources are fruit and vegetables. Moreover it is added to many food products. Cooking destroys vitamin C.
- Separation modus: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borat-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, effective length: 8 cm
- Injection: 5 s, -50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: Short end dection of ascorbic acid and its spectral data can be seen.
Download: Vitamin-C1.pdf
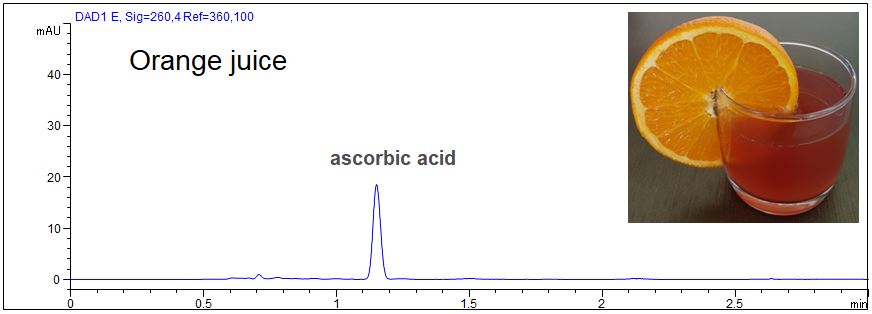
Determination of vitamin C in beverages
- Separation modus: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borat-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, effective length: 8 cm
- Injection: 5 s, -50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: Short end dection of ascorbic acid in lime juice and orange juice.
Download: Vitamin-C2.pdf
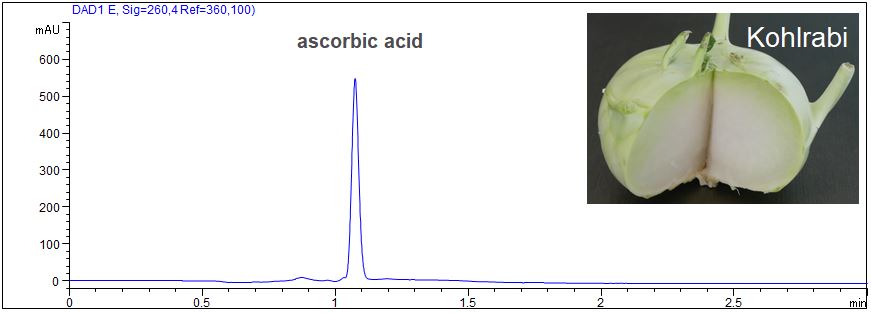
Determination of vitamin C in vegetables
- Separation modus: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borat-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, effective length: 8 cm
- Injection: 5 s, -50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: Short end dection of ascorbic acid in kohlrabi and tomatoes. Sample preparation:The vegetables were finely chopped and the resulting juice was injected without further dilution.
Download: Vitamin-C-Kohlrabi.pdf
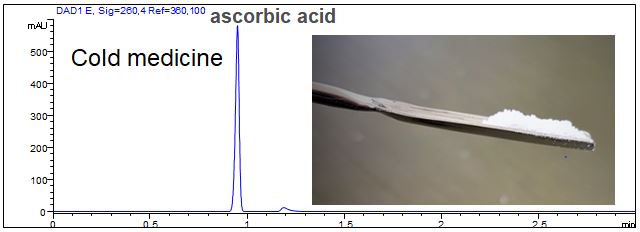
Determination of vitamin C in cold medicine
- Separation modus: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borat-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, effective length: 8 cm
- Injection: 5 s, -50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: Short end dection of ascorbic acid in a cold medicine. Sample preparation: 250 mg were dissolved in 20 ml water.
Download: Vitamin-C4.pdf
Determination of vitamins in food supplements
- Separation modus: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borat-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, effective length: 56 cm
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The two samples and the standard solution were dissolved in water.
Download: Vitamins-Food-Supplement.pdf
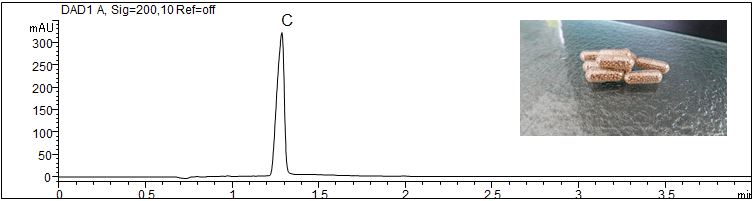
Determination of vitamin C in food supplements
- Separation modus: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borat-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, effective length: 56 cm
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The two samples were dissolved in water.
Download: Vitamins-Food-Supplement-1.pdf
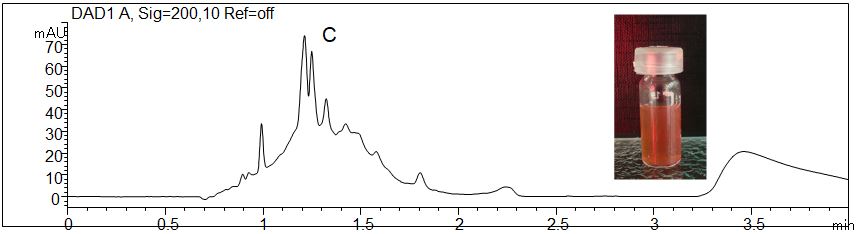
Determination of vitamin C in red juice for children
- Separation modus: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borat-SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, effective length: 56 cm
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The juice was dilluted 1:5. For the quantification of vitamin c different wave lenghts were evaluated.
Download: Vitamins-Food-Supplement-2.pdf