Apart from some exceptions inorganic anions and organis acids show insufficient absorption in the UV range. Therefore in most cases indirect UV detection is used for the separations. Depending on the application several electrolytes are available.
Standard of anions and phosphates
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Plating Bath Buffer (Agilent)
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 72 cm effective length
- Detection: indirect UV, 245 nm
- Standard solution:chloride (10 mg/l), nitrate (10 mg/l), sulfate (10 mg/l), triphosphate (30 mg/l), diphosphate (10 mg/l), hypophosphite (10 mg/l), phosphite (20 mg/l), and phosphate (10 mg/l).
- Description: In the PDF it is shown how a longer capillary influences the improvement of the resolution. Especially the critical resolution between nitrate and sulfate could be improved in this way.
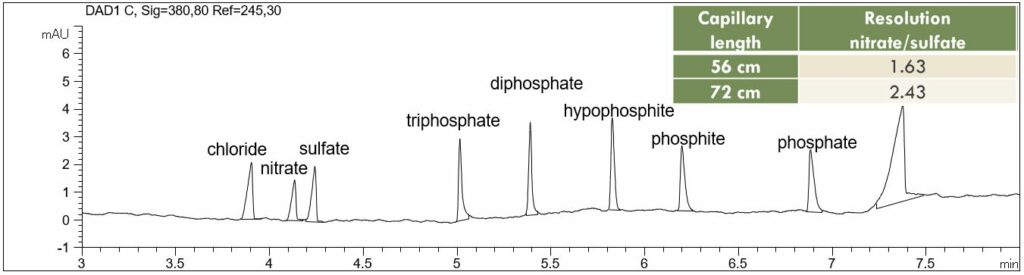
Download (314 KB): phosphate-standard.pdf
Sulfate in electroplating chrome baths
Chromium(VI) plating solutions can be applied for hard plating as well as for bright (decorative) plating. The main components are chromium trioxide and sulfuric acid. So, by analyzing sulfate, the content of sulfuric acid can be monitored.
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: laboratory made, pH 8
- Capillary: coated, 50 µm ID, 56 cm effective length, 64.5 cm in total
- Detection: indirect UV, 275 nm
- Separation: 25°C, -30 kV
- Description: The bright chrome bath and the hard chrome bath were diluted 1:200. The peak identity of sulfate was verified by standard addition. Another acid component can be detected in the hard chrome bath (marked with “?”), migrating directly next to sulfate.
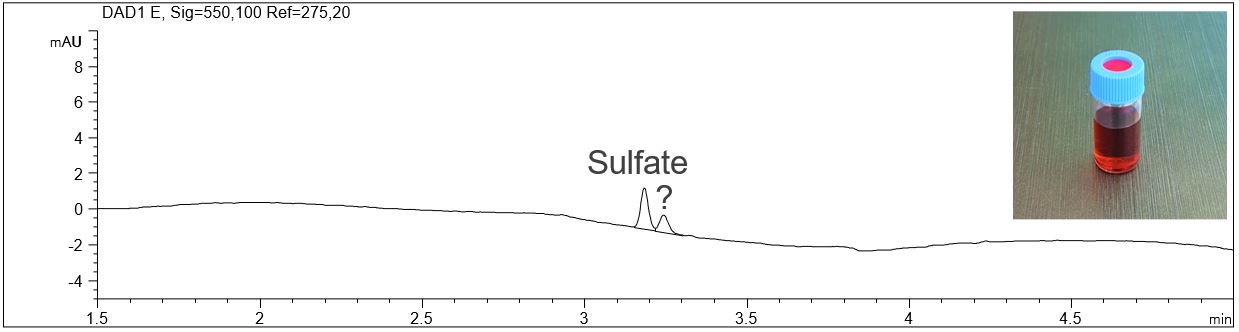
Analysis of sulfate in chrome baths
In the PDF the e-grams of a sulfate standard solution, a bright chrome bath and a hard chrome bath can be seen.
Download (333 KB): sulfate-chrome-bath.pdf
Anions in a liquid laundry detergent and a plant fertilizer
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Plating Bath Buffer (Agilent)
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 72 cm effective length
- Detection: indirect UV, 245 nm
- Sample solution: a) liquid laundry detergent (dilution 1:100), b) plant fertilizer (sample preparation: 500 mg/l)
- Description: In the PDF (200 KB) it is shown that relevant anions like sulfate, triphosphate, diphosphate and phosphate can be determined simultaneously in the liquid laundry detergent and the plant fertilizer.
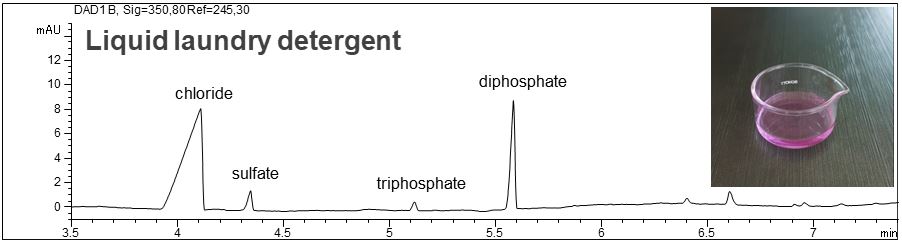
Phosphate and anions in a laundry detergent
Download (200 KB): phosphate-detergent-plant-fertilizer
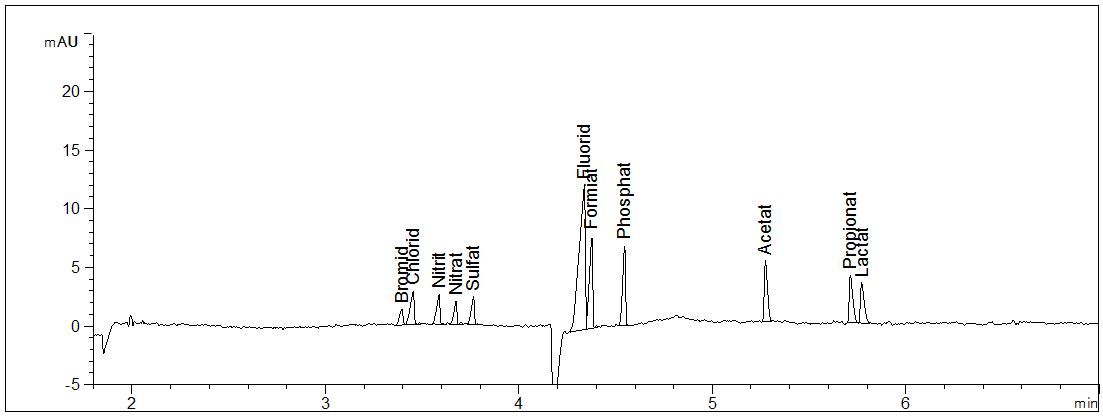
Standard of anions
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Basic anion buffer (Agilent)
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 114 cm in total
- Detection: indirect UV, 275 nm
- Description: The anions bromide, chloride, nitrite, nitrate, sulfate, fluoride and phosphate as well as some anions of organic acids like formiate, acetate and lactate are analysed with indirect UV detection. Due to the long capillary the simultaneous determination of these anions is possible.
Download: Anionenstandard.pdf
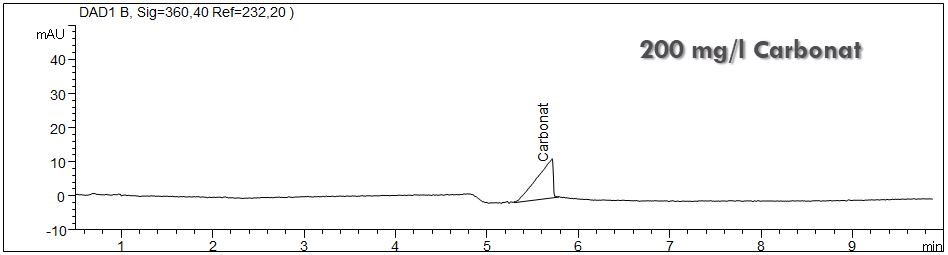
Carbonate
The determination of carbonate with capillary electrophoresis is done with indirect UV detection. The challenge of this analysis is to eliminate blank values of carbonate. When the sample is stored in an open vessel even for only a short period carbon dioxide enters the solution and is transfered to carbonate. Especially in alkaline solution this transformation is very quick, therefore it is practically impossible to work without a blank. This does not only apply for the sample solution but also for all other solutions used for the method like electrolyte and sample solvents.
Therefore a higher mistake is found for the determination of carbonate in contrast to the other anions. Nevertheless it is possible to analyse carbonate with a good linearity.
Standard of carbonate
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Salicylic acid, pH 8
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64 cm in total, coated with polybren
- Detection: indirect UV, 232 nm
- Description: The detection of carbonate is done with indirect UV detection. The quick preparation of the fresh electrolyte provides good determination of carbonate above 10 mg/l.
Download: Carbonatstandard.pdf
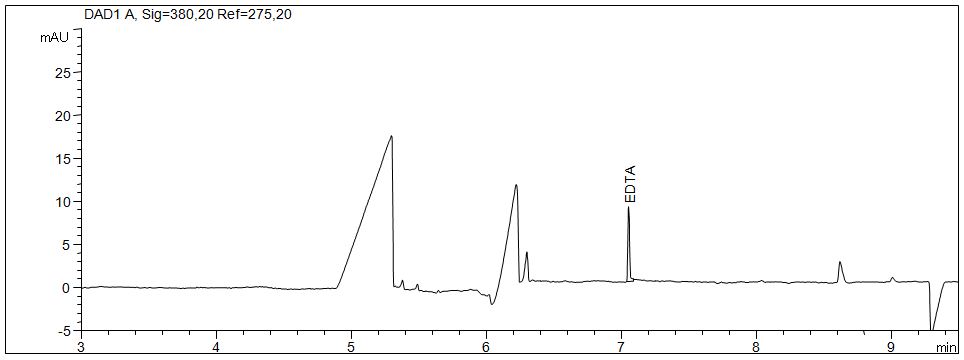
EDTA and anions
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Basic anion buffer (Agilent)
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 97 cm in totalt
- Detection: indirect UV, 275 nm
- Description: EDTA can be separated from the anions and the organic acids.
Download: EDTA-und-Anionen
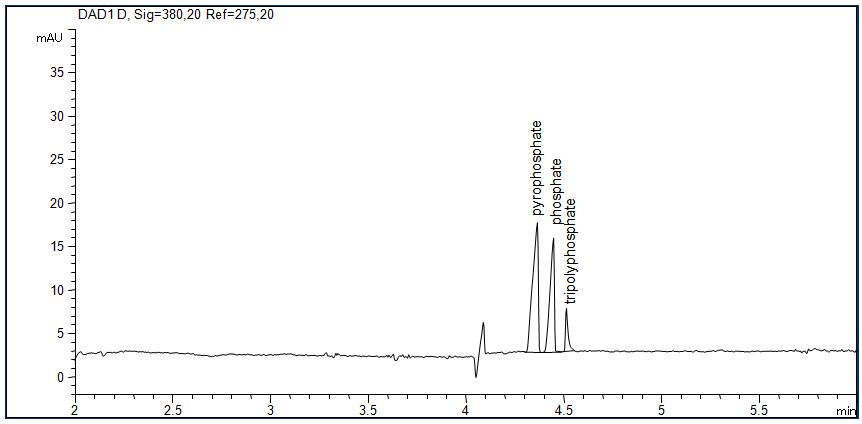
Phosphate
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Basic anion buffer (Agilent)
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 72 cm in total
- Detection: indirect UV, 275 nm
- Description: Phosphate, triphosphate and polyphosphate con be determined simultaneously.
Download: Phosphate.pdf
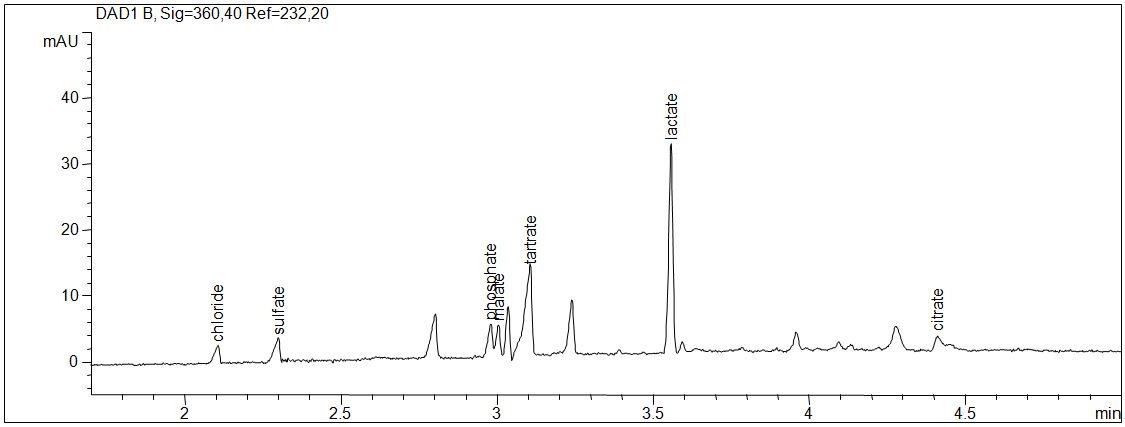
Anions in red vine
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Salicylic acid with EOF modifierr
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64 cm in total
- Detection: indirect UV, 232 nm
- Description: Besides the seven known anions chloride, sulfate, phosphate, malate, tatrate, lactate and citrate several unknown substances are detectable.
Download: Anionen-in-Rotwein.pdf
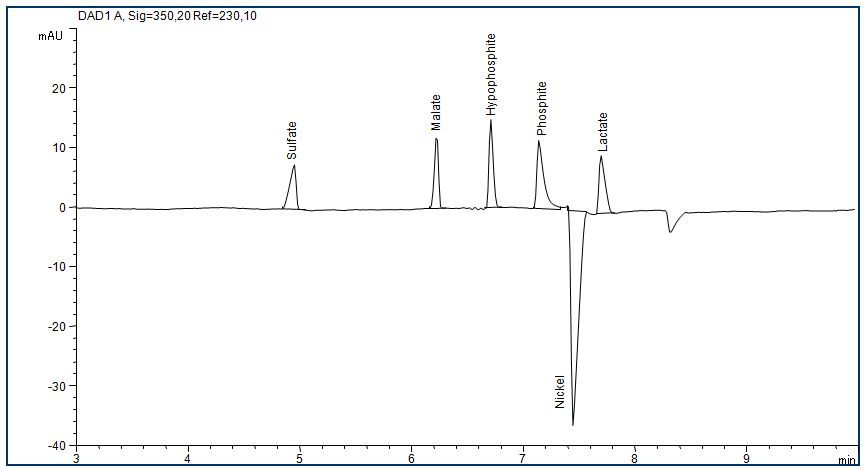
Anions in an electrolysis bath
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Plating bath buffer (Agilent)
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 80 cm in total
- Detection: indirect UV, 230 nm
- Description: The determination of the shown anions sulfate, hypophosphate and phosphate as well as anions of some organic acids like malate and lactate is particularly interesting for samples in the electroplating industry.
Download: Elektrolysebad
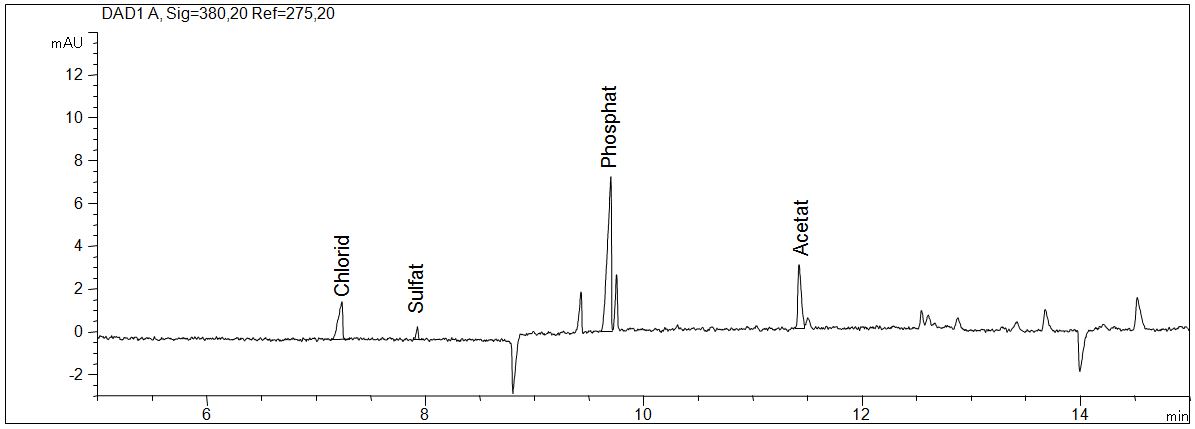
Anions in yeast wheat beer
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Basic anion buffer (Agilent
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 114 cm in total
- Detection: indirect UV, 275 nm
- Description: Chloride, sulfate, phosphate and acetate are found in yeast wheat beer.
Download: Anionen-in-Hefeweissbier.pdf
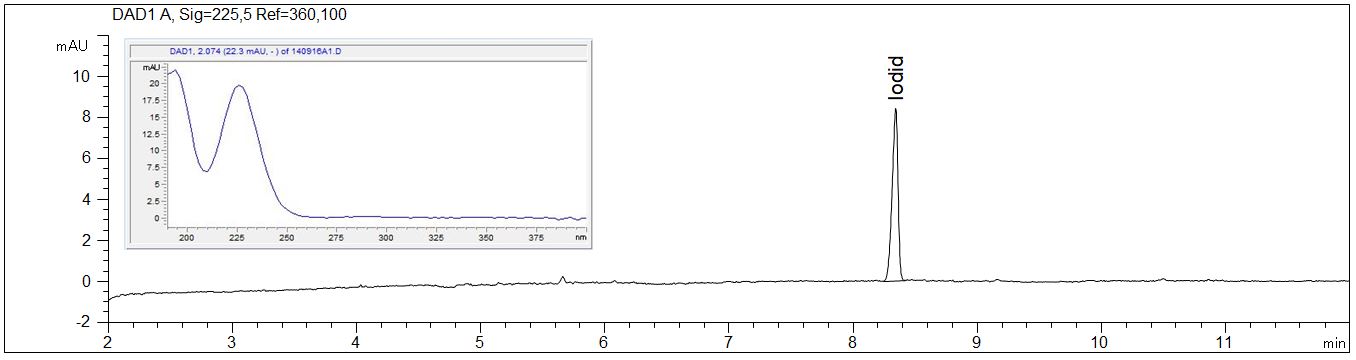
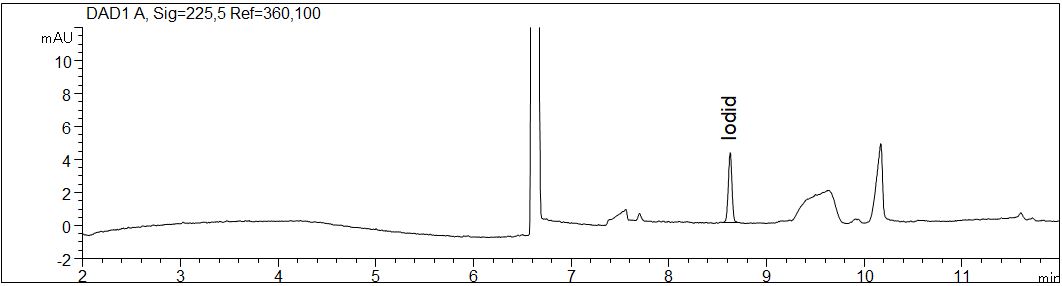
Iodide as standard solution
Due to its high extinction coefficient iodide is detectable down to a very low range with direct UV detection.
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Borate with EOF modifier and selectivity modifier
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Detection: direct UV, 225 nm
- Description: The figure shows a standard solution of iodide in an concentration of 1 mg/l. The spectrum of iodide has a maximum at 225 nm.
Download: Iodid-Standard.pdf
Iodide in Urine
Sufficient supply of iodide is essential for the human body. Iodide as trace element is necessary for the thyroid for the production of the hormones T3 and T4. Since the daily intake of iodide by food can only be detected inaccurately, the determination of iodide is done retrospectively by the analysis of iodide in urine. According to WHO an amount of 100 – 200 µg/l iodide in urine represents the sufficient supply of iodide.
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Borate with EOF modifier and selectivity modifierr
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in totalt
- Detection: direct UV, 225 nm
- Description: The analysis of iodide in urine with capillary electrophoresis is successful in less than 10 min despite of the urine matrix. The demanded concentration range can easily be covered under the given conditions. The pdf shows the standard solution of iodide and two different levels of iodide in urine.
Download: Iodid-Urin.pdf
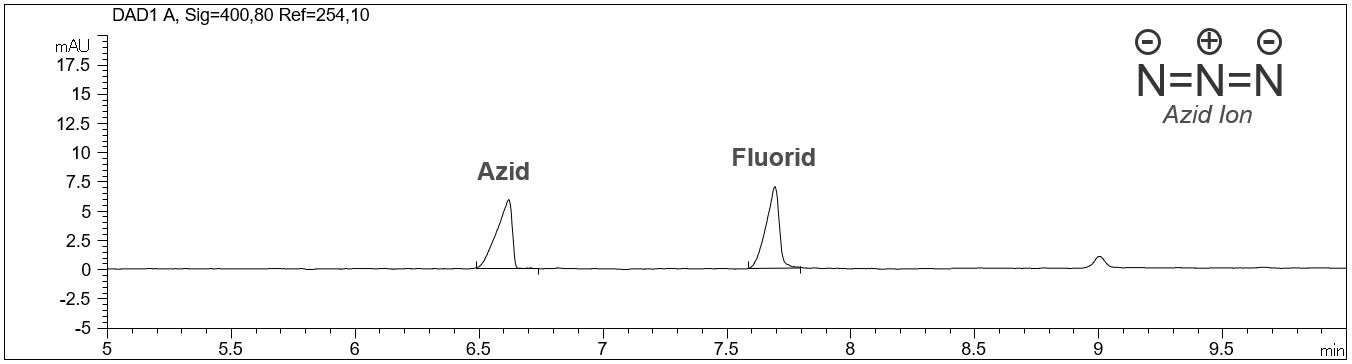
Azide-Anion
The azide anion N3− shows similar chemical behaviour like the halogenid ions and is therefore also called pseudo halogenide. Besides its importance in chemical synthesis it is used for the conservation of polymers and in biochemistry due to its antibiotic quality.
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Analis accelerator 10-004608
- Capillary: fused silica, 75 µm ID, 64 cm in total
- Detection: indirect UV, 254 nm
- Description: The analysis of azide with capillary electrophoresis can be excecuted with indirect UV detection and an electrolyte containing a modifier for the EOF. The pdf shows a standard solution of azide and fluoride.
Download: Standardlösung Azid und Fluorid.pdf
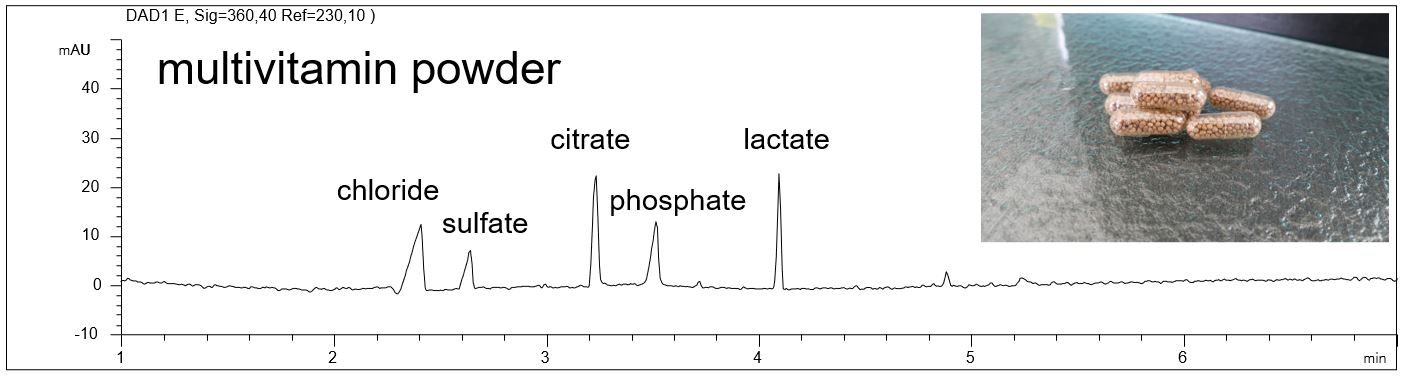
Anions and organic acids in food supplements
The anions and organic acids like citrate, lactate and ascorbic acids can be analyzed in only 6 min in food supplements using the indirect detection mode.
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: salicylate
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64 cm in total
- Detection: indirect UV, 230 nm
- Description: The pdf shows the anions and organic acids in a solution of a multivitamin powder and in a vitamin C capsule.
Download: Anions-Food-Supplements.pdf