Prior to the analysis of proteins many aspects have to be considered. One the one hand the isoelectric point of the proteins should be known to decide whether the proteins are measured as cations or anions. On the other hand the tendency of proteins to interact with the wall of the capillary has to be taken into account, in some cases coated capillaries are preferable. Finally it has to be decided whether the proteins are analysed in their natural folded in their denaturated form. This decision has consequences on the choice of several method parameters like the composition of the electrolyte or the temperature.
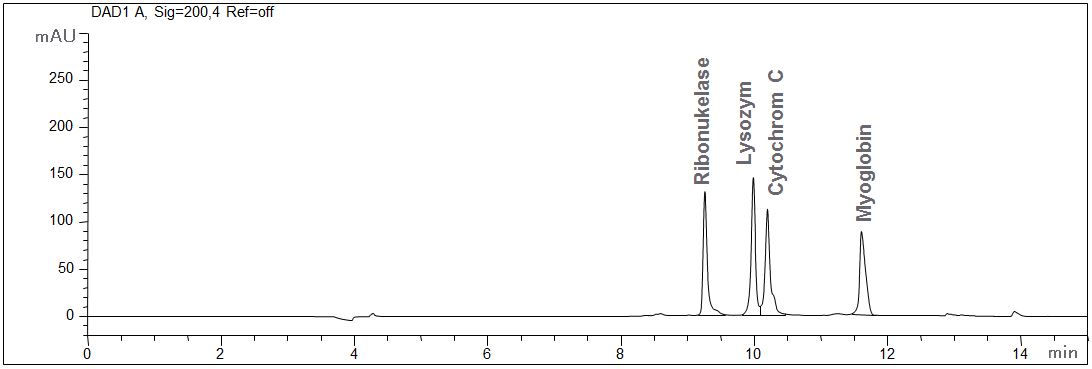
Standard proteins
- CE mode: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borate-SDS
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The standard solution contains 100 mg ribonuclease, lysozyme, cytochrome and myoglobin, each. The interaction of the proteins with the wall of the capillary is suppressed due to the micellar electrolyte.
Download: Proteine_Standard.pdf
The effect of desalting on the determination of Erythropoietin (EPO)
- CE mode: CZE (EP-Monograph No 1316)
- Electrolyte: according to PhEur
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 80 cm in total
- Temperature: 35°C
- Injection: hydrodynamic
- Detection: direct UV, 214 nm
- Separation: 11.5 kV
- Description: A repeated desalting is necessary to ensure separation of glycoforms. Multiple desalting not only has a positive effect on the resolution of the glycoforms. The profile of the baseline is also improved and system peaks are reduced.
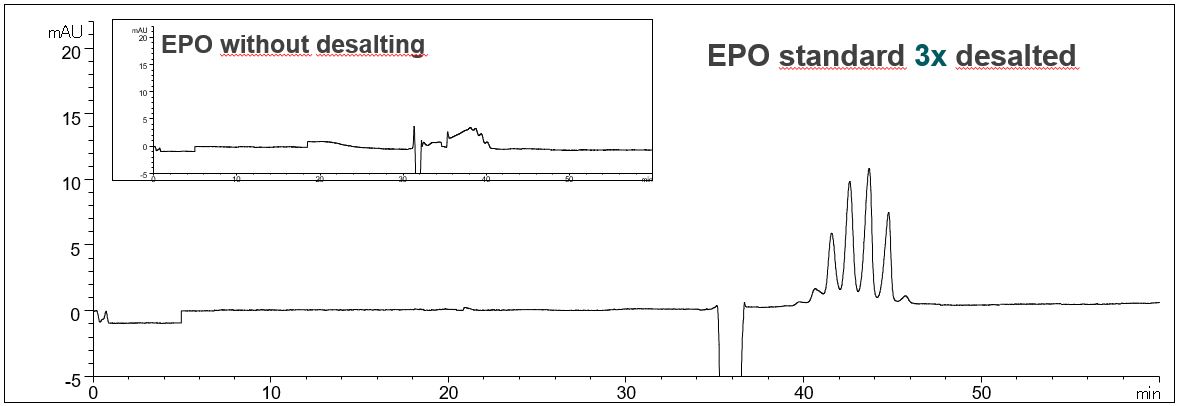
Effect of desalting on the resolution of EPO glycoforms
In the PDF (497 kB) the e-grams of the EPO standard solution without desalting, after desalting and after triple desalting are shown.
Download: EPO-desalting
The effect of the capillary length on the determination of Erythropoietin (EPO)
- CE mode: CZE (EP-Monograph No 1316)
- Electrolyte: according to PhEur
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, different lengths
- Temperature: 35°C
- Injection: hydrodynamic
- Detection: direct UV, 214 nm
- Separation: 143 V/cm (different kV, depends on the capillary length)
- Description: The determination of the different glycoforms of EPO is done according to EP monography No.1316. In the Monograph a capillary length of about 100 cm is given. However, by adjusting the voltage to maintain the appropriate field strength the use of shorter capillaries is possible, leading to shorter analysis times and higher sensitivity. The best result was obtained using the 64.5 cm capillary. In this way, the migration time of the highest peak has been reduced from 58 min to 32 min.
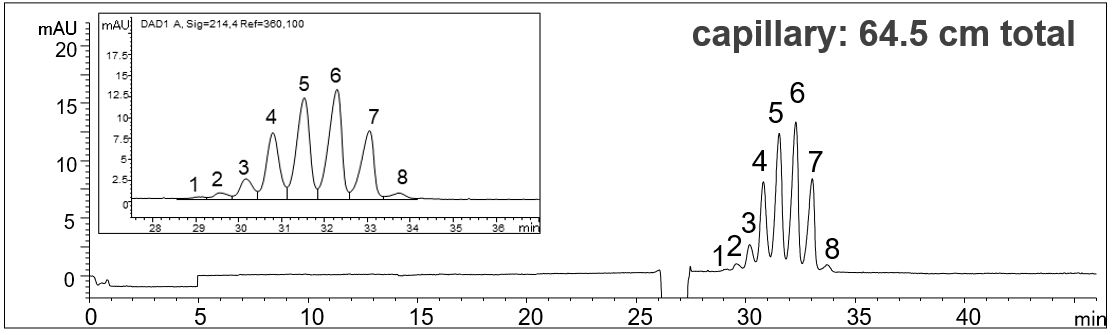
Effect of the capillary length on the analysis of EPO glycoforms
In the PDF (520 KB) the e-grams of three different capillary lengths (112.5 cm, 80.5 cm, 64.5 cm) are summarized. The voltage was adjusted in each case so that a field strength of 143 V/cm resulted.
Download: EPO-capillary-length
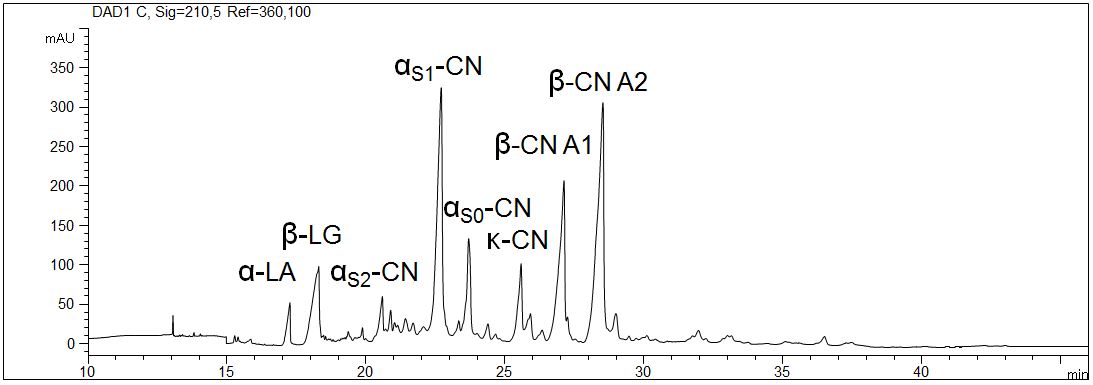
Proteins in milk (1,5%)
The most important proteins in milk are caseine, β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin. They are analyzed with capillary electrophoresis in several dairy products. Due to the specific composition of the gel even the determination of the individual phosphorylic forms of caseine is possible.
- CE mode: Gel electrophoresis (CGE)
- Electrolyte: 6 M urea, MHEC, citrate, pH 3
- Capillary: coated, 50 µm ID, 64 cm in total
- Detection: direct UV, 210 nm
- Description: A traditionally produced raw milk with 1,5 % fat was analyzed. The sample was prepared with urea and DTT. The interaction of the proteins with the wall of the capillary was inhibited due to the application of a coated capillary. The high selectivity allows the distinction of the different caseines.
Download: Proteine_Milch_1.pdf
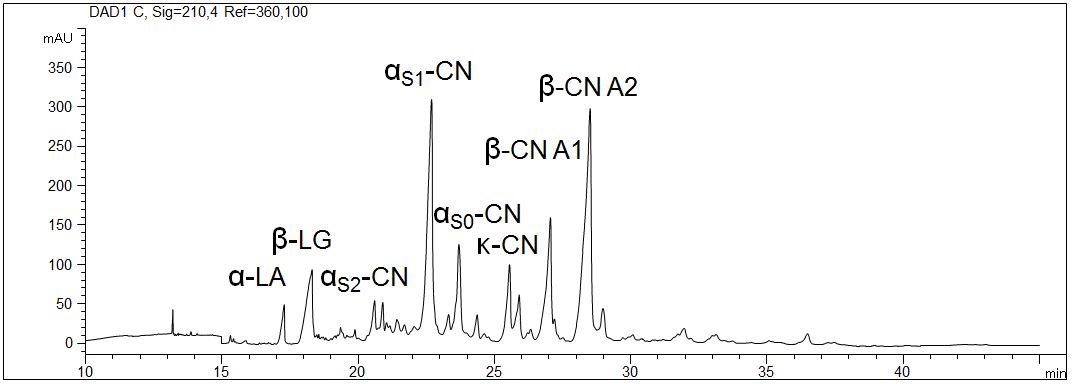
Proteins in milk (3,5%)
- CE mode: Gel electrophoresis (CGE)
- Electrolyte: 6 M urea, MHEC, citrate, pH 3
- Capillary: coated, 50 µm ID, 64 cm in total
- Detection: direct UV, 210 nm
- Description: The pasteurized milk with 3,5 % fat was prepared with urea and DTT. The interaction of the proteins with the wall of the capillary was inhibited due to the application of a coated capillary. The high selectivity allows the distinction of the different caseines.
Download: Proteine_Milch_2.pdf
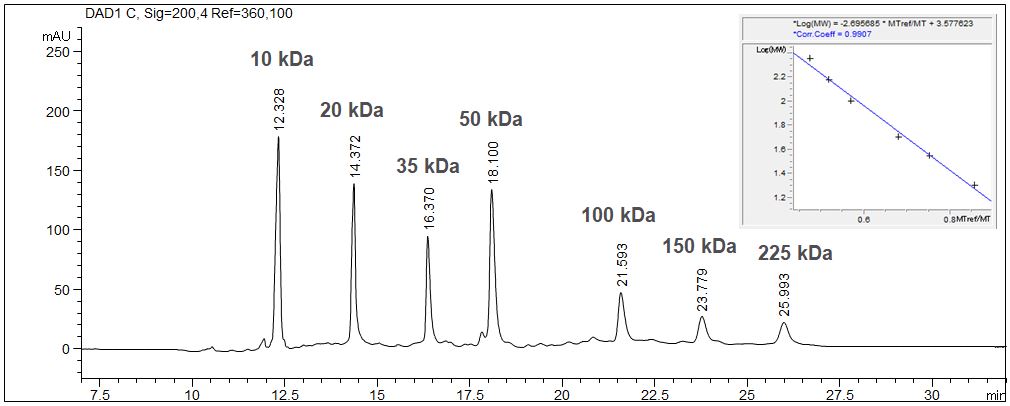
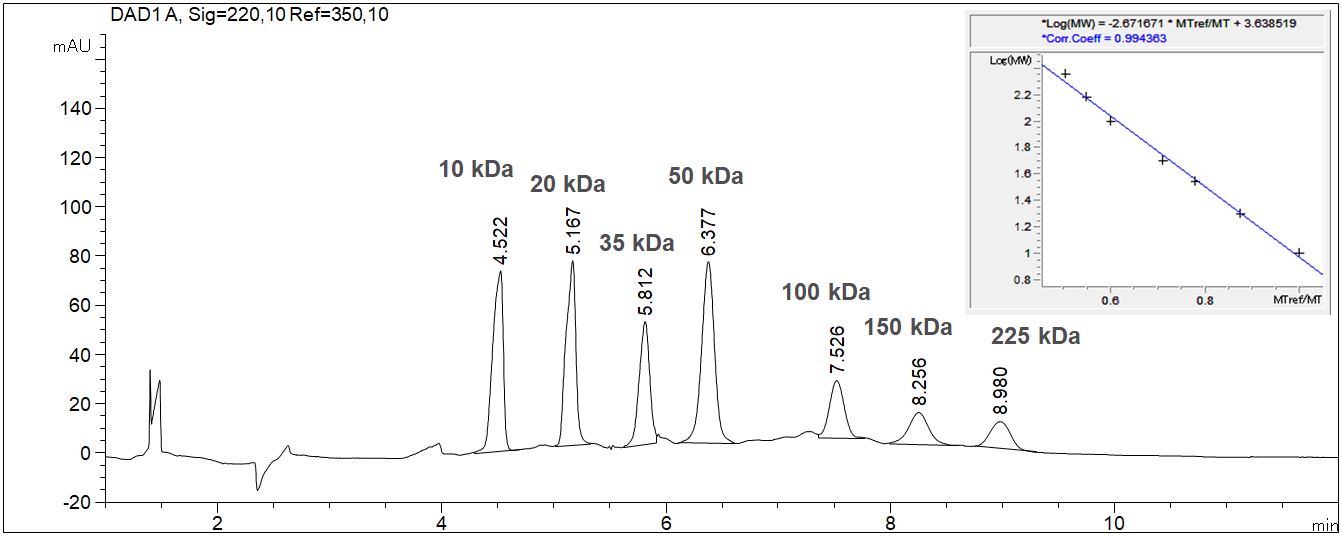
SDS-MW: Determination of the size of proteins with CE
When using the SDS-MW technique the determination of the size of proteins is possible with CGE due to logarithmical calibration.
- CE mode: Gel electrophoresis (CGE)
- Electrolyte: Sample suffer: 100 mM Tris-HCl pH 9.0, 1% SDS
- Gel: SDS-MW Gel Buffer pH 8.0, 0,2% SDS (Sciex, A30341)
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 33 cm in total, 24 cm effective
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Injection: elektrokinetic, -8 kV, 20 s
- Description: The given example shows the calibration of a molecular weight standard with the value table and the calibration curve. The molecular weight standard contains seven standard substances from 10 kDa up to 225 kDa. The 10 kD standard is used as internal standard. Due to the high viscosity of the gel it is essentially to inject the sample electrokinetically. In case of high ionic strength in the sample a desalination has to be executed prior to the injection to prevent discrimination of the protein during the injection process.
Download: SDS-MW.pdf
SDS-MW: Dezermination of the size of proteines with CE in a quick screening
- CE mode: Gel electrophoresis (CGE
- Electrolyte: Sample suffer: 100 mM Tris-HCl pH 9.0, 1% SDS
- Gel: SDS-MW Gel Buffer pH 8.0, 0,2% SDS (Sciex, A30341)
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 33 cm in total, 24 cm effective
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Injection: elektrokinetic, -8 kV, 20 s
- Description: The calibration of a molecular weight can be done as a quick screening when the separation lenght is shortened to 8 cm. The whole calibration is complete in 10 min. The given example shows the calibration of the molecular weight standard with the value table and the calibration curve. The standard contains seven standard substances from 10 kDa up to 225 kDa.
Download: SDS-MW-Screening.pdf