The analysis of ionic liquids („IOLI“, „IL“) can be performed by capillary electrophoresis (CE) using different separation modes with both direct and indirect UV detection. The main components, impurities or additives used for special application solutions can be quantified.
Impurity control of the ionic liquid “1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroaluminate” (EMIM AlCl4)
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: CE-Kd01
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID (bubble cell), 64 cm in total
- Injection: 10 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: Determination of the major cationic component 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium (EMIM) and the relevant impurities Imidazole (IM), 1-Methylimidazole (1-MIM), 4-Methylimidazole (4-MIM) and Ethylimidazole (EIM) in the IOLI sample using an acidic separation buffer and direct UV-detection.
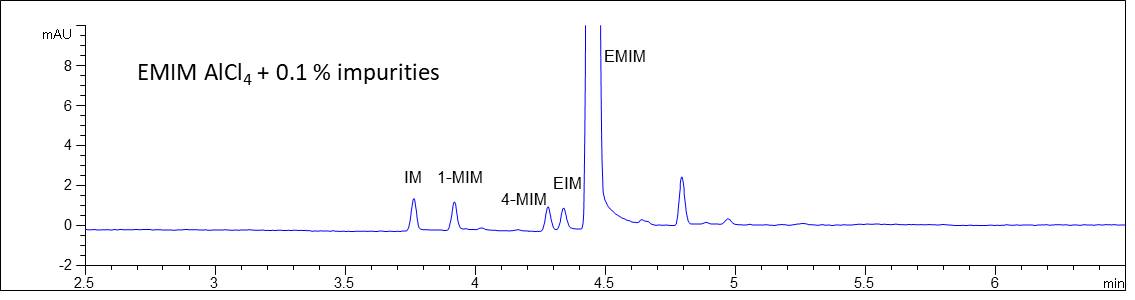
Impurities in EMIM AlCl4
Download: EMIM AlCl4-Impurities
Additive Nicotinamide (NA) in the ionic liquid “1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroaluminate” (EMIM AlCl4)
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: CE-Kd01
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID (bubble cell), 64 cm in total
- Injection: 10 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: When using EMIM AlCl4 as an electrolyte solution for the deposition of aluminum, nicotinamide can be used as an additive to improve the coating properties. Nicotinamide can be determined in the ionic liquid using an acidic electrolyte system and direct UV-detection.
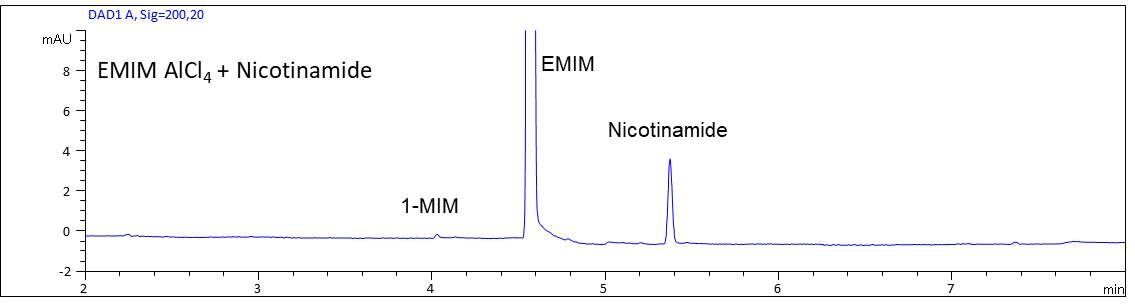
Determination of the additive nicotinamide in EMIM AlCl4
Download: EMIM AlCl4-Nicotinamide
Additive 2-Chloropyridine-3-Carbonylchloride (CPCC) in the ionic liqid “1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroaluminate” (EMIM AlCl4)
- Separation: MEKC
- Electrolyte: CE-Mz01
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID (bubble cell), 64 cm in total
- Injection: 10 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: When using EMIM AlCl4 as an electrolyte solution for the deposition of aluminum, CPCC can be used as an additive to improve the coating properties. CPCC can be determined in the ionic liquid using an micellar electrolyte system and direct UV-detection.
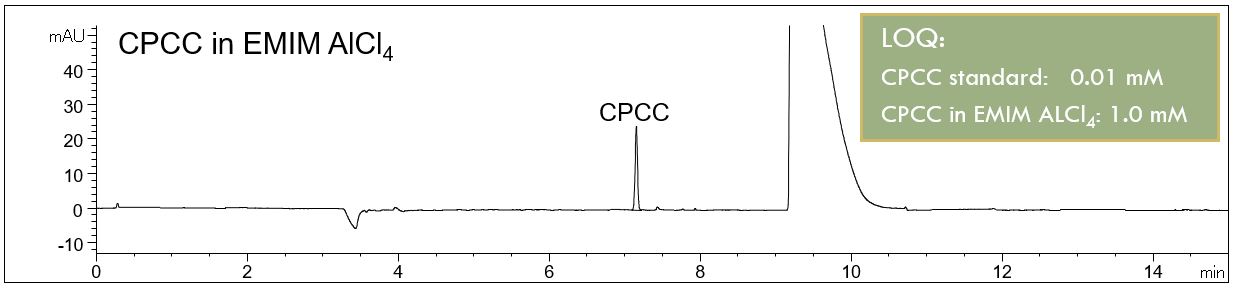
CPCC in EMIM AlCl4
In the PDF (414 KB) the e-grams of the diluted ionic liquid solution and a standard addition are shown. The limit of quantification (LOQ) of the analysis of CPCC is given. It was shown that the method can be used for the analysis of CPCC in the ionic liquids of interest.
Download (414 KB): EMIM AlCl4-CPCC
Determination of the cationic main components EMIM and Aluminum in the Ionic Liquid “1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloroaluminate” (EMIM AlCl4)
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: CE-Ki01
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 15 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: indirect UV, 260 nm
- Description: Applying the method described the amount of the two cationic main components EMIM and aluminum in the IOLI EMIM AlCl4 can be determined using a separation buffer optimized for the indirect UV-detection of cations. The method can be used for in-process analysis of the coating process.
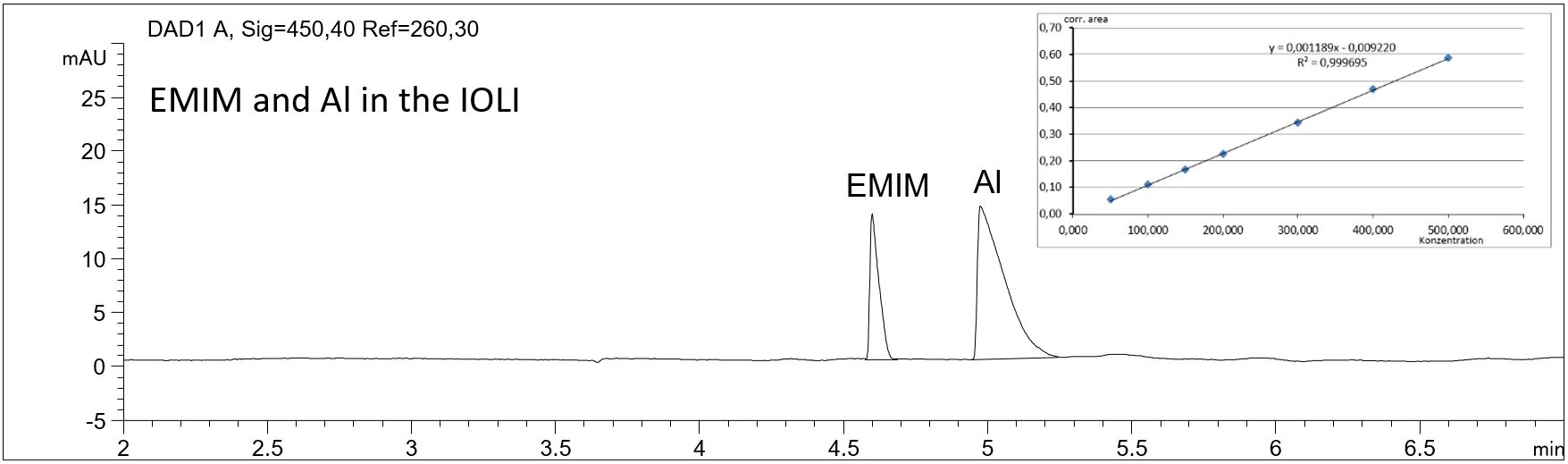
Cationic main components EMIM and aluminum in an ionic liquid
In the PDF (565 KB) the e-grams of the diluted ionic liquid solution and a standard solution are shown. The quality parameters of the calibration graphs are summarized for EMIM and aluminum.
Download (565 KB): EMIM-Aluminum
Determination of inorganic cationic impurities in the IOLI EMIM AlCl4 using the indirect UV detection
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: CE-Ki01
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 15 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: indirect UV, 260 nm
- Description: The detection limit (LOD) and quantification limit (LOQ) for possible inorganic cationic impurities in the IOLI EMIM AlCl4 was determined by addition of the relevant cations. The following cations were investigated: potassium, calcium, sodium, magnesium and ethylimidazole (EIM).
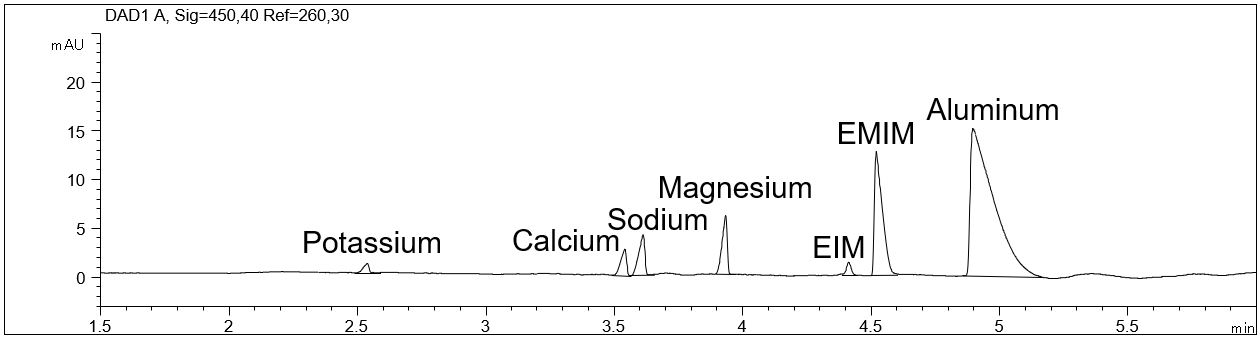
Inorganic cationic impurities in an ionic liquid
In the PDF (507 KB) the e-grams of a 2 % and a 0.5 % addition of inorganic cations to the IOLI EMIM AlCl4 are shown. The calculated LOD and LOQ are given in a table.
Download (507 KB): EMIM-Al-impurities
Determination of the anionic main component chloride in the Ionic Liquid EMIM AlCl4
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: CE-Ai01
- Capillary: PVA coated, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 10 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: indirect UV, 210 nm
- Description: Applying the method described the amount of chloride in the IOLI EMIM AlCl4 can be determined using a separation buffer optimized for the indirect UV-detection of anions. The method can be used for in-process analysis of the coating process. Chloride can be used as a marker for the leaktightness of the system. If moisture (e.g. air humidity) enters the system, chloride escapes in gaseous form as hydrogen chloride and this will reduce the content in the IOLI.
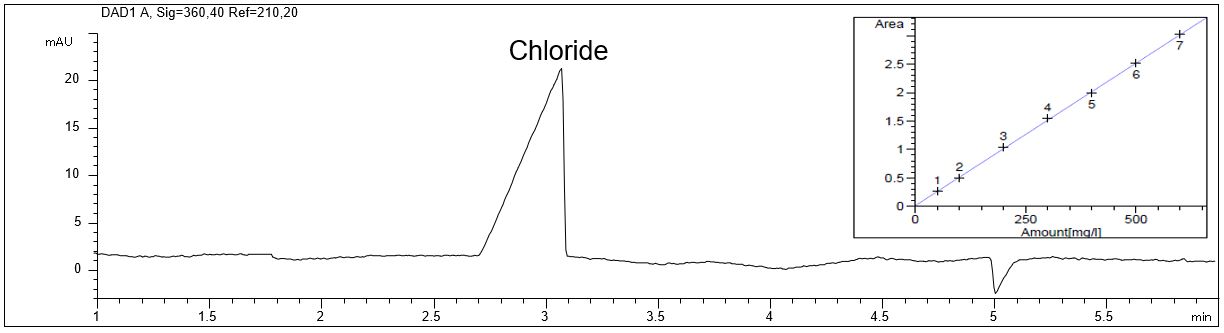
Chloride as anionic main component in an ionic liquid
In the PDF (499 KB) the e-grams of the SST solution, the diluted ionic liquid solution and a chloride standard solution are shown. The quality parameter of the calibration graphs for chloride is given.
Download (499 KB): EMIM-Al-chloride
Determination of anionic impurities in the IOLI EMIM AlCl4 using the indirect UV detection
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: CE-Ai01
- Capillary: PVA coated, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 10 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: indirect UV, 210 nm
- Description: The detection limit (LOD) for possible inorganic anionic impurities in the IOLI was calculated on the example of sulfate. It was found that the IOLI was very pure. No anionic impurities were detectable.
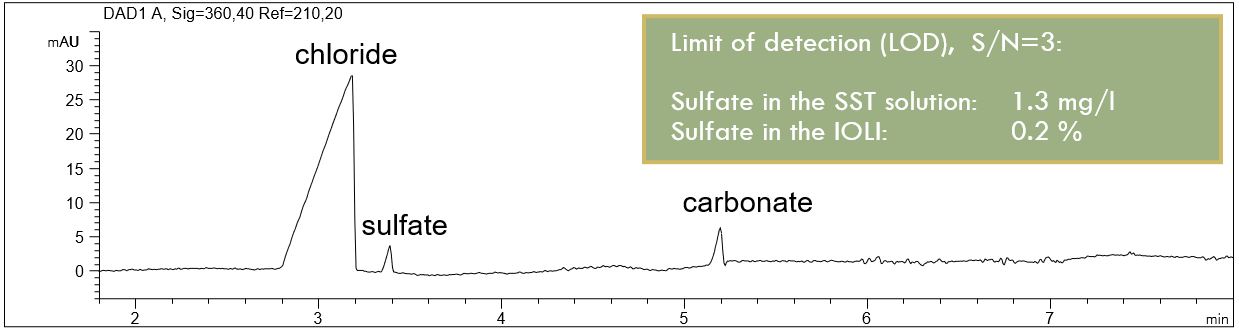
Anionic impurities in EMIM AlCl4
In the PDF (316 KB) the e-grams of blank, of a standard solution with interesting anions and organic acids and an SST solution containing the same chloride concentration as the IOLI sample are summarized. The calculated LOD for sulfate is given in a table.
Download (316 KB): EMIM-Al-anionic-impurities
Determination of cationic impurities in the IOLI „Butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bromide“ (BMPL Br)
-
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Imidazole system
- Capillary: 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: hydrodynamic 15 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: indirect UV, 215 nm
- Description: With a cationic CZE separation and indirect UV-detection, the Butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium (BMPL) cation, ammonium, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and the reactant 1-methylpyrrolidine (1-MPL) used in the synthesis of BMPL can be determined in the IOLI-sample.
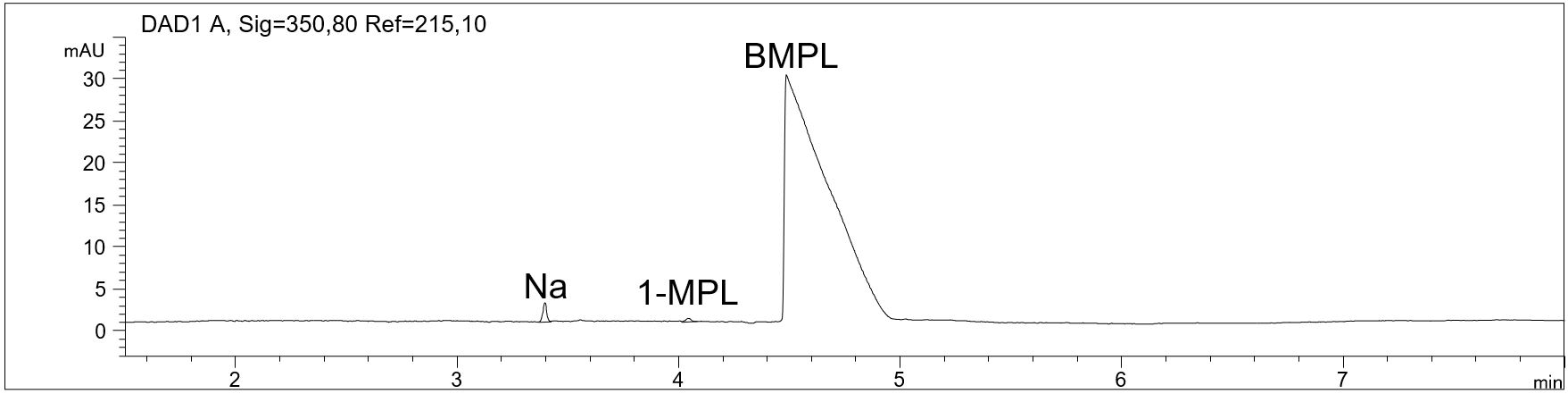
Determination of cationic impurities in BMPL Br
In the PDF (602 KB) the e-grams of the sample solution and the quantitative standard addition of 0.5 % 1-MPL to the sample are shown.
Download (602 KB): BMPL-Br
Determination of cationic impurities in the IOLI „Butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium tetracyanoborate“ (BMPL TCB)
-
-
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Imidazole system
- Capillary: 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: hydrodynamic 15 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: indirect UV, 215 nm
- Description: The sample solution was prepared with a concentration of 1000 mg/l. The Butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium cation and cationic analytes can be quantified using a cationic CE separation and indirect UV-detection. In particular, the detection of the synthesis component 1-methylpyrrolidine (1-MPL) is important for the analysis. The concentration of 1-MPL should be less than or equal to 0.1 %.
-
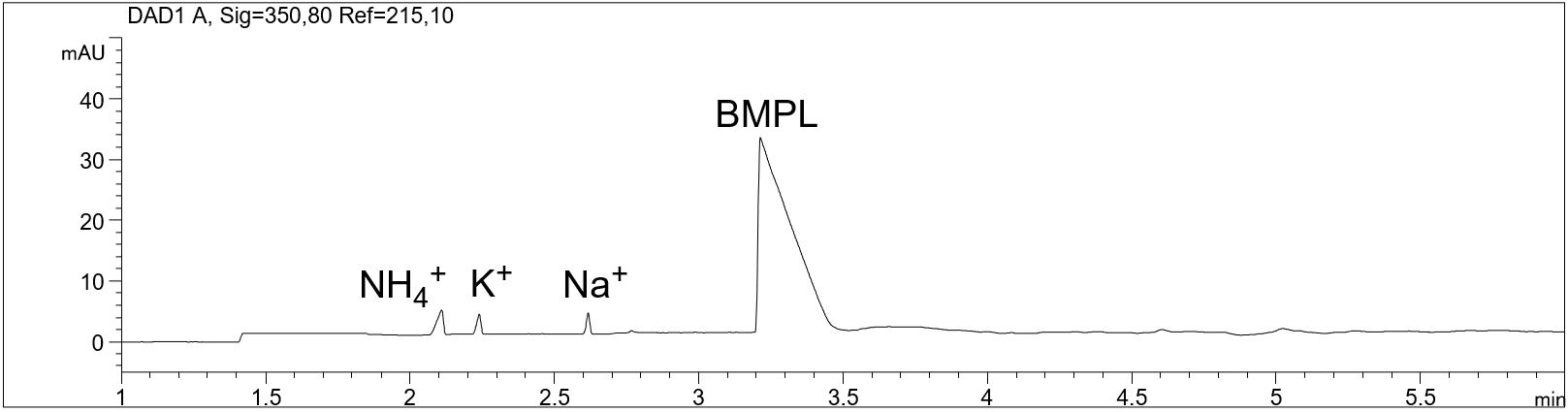
Determination of cationic impurities in BMPL TCB
In the PDF (313 KB) the e-grams of the standard addition of 0.5 % 1-MPL to the IOLI sample as well as the standard addition of ammonium and potassium (representative for potential impurities) are shown.
Download (313 KB): BMPL-TCB