Frequently samples comprise of mixtures of analytes which cannot be assigned to a specific category. Therefore „miscellaneous“ is a collection of exceptional applications.
Saccharin in a Bright Nickel Bath
CAS No: 81-07-2 128-44-9 (sodium salt)
- Separation: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borate/SDS
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 40 cm effective length, 48 cm in total
- Injection: 10 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The Bright nickel bath samples were diluted 1:200. The peak identity of Saccharin was verified by standard addition and by comparing the spectral UV data of the peak in the sample solution and in the standard solution.
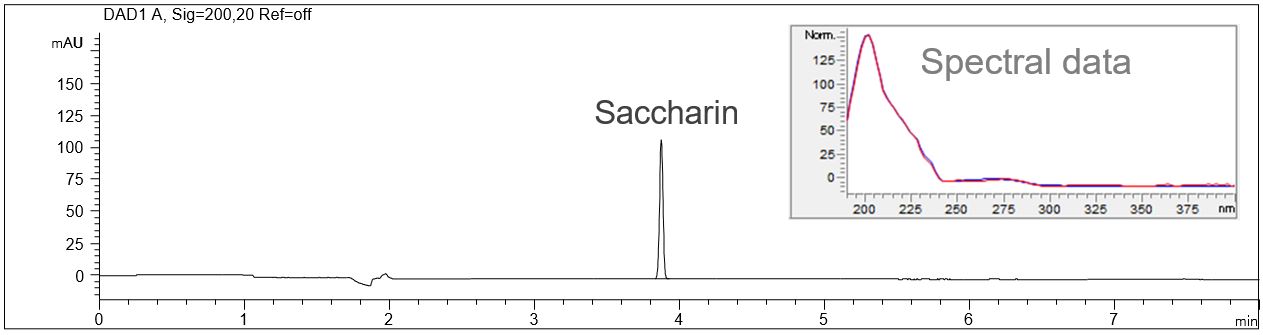
Saccharin in a Bright Nickel Bath
In the PDF the electropherograms of a Saccharin standard solution, a bright nickel bath solution, standard addition and spectral data are shown.
Download (340 KB): Saccharin-bright-nickel-bath.pdf
Lecithin (Phospholipide)
Lecithin (Phospholipide) can be found in natural products, especially in eggs and cells of vegetable seeds. A common starting material for the extraction of lecithin is, for example, soy. Especially their properties as lubricant, emulsifier, antioxidant and flavor protector provide a wide range of applications. So, phospholipids are widely used, eg, in the food industry and in cosmetic products. Quantification by CE is possible using direct UV detection at low wavelengths.
CAS No: 8030-76-0,
Other names: Lecithin (soya), Lecithins, PC, SPC-98A, SPC-95, SPC-90A, SPC-80A, SPC-70A
- Separation: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borate/SDS
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 40 cm effective length, 48 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 195 nm
- Description: standard solution of Soybean Lecithin, 50 mg/l
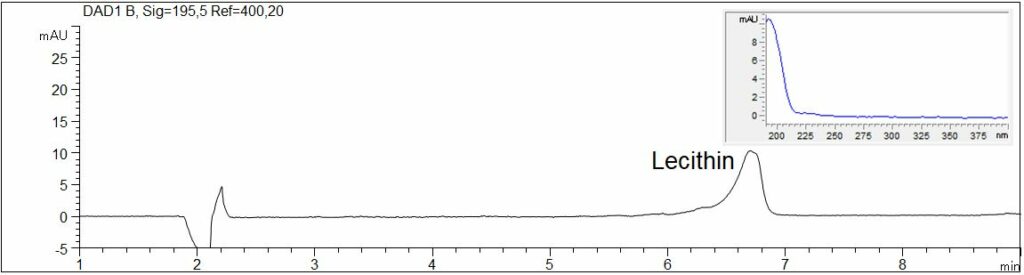
Soybean Lecithine
In the PDF the electropherogram of Soybean Lecithin (50 mg/l) and its spectral data are shown.
Download (200 KB): lecithin
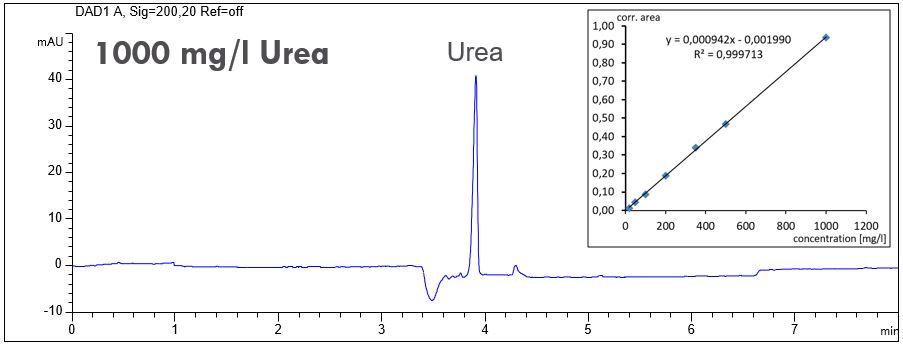
Urea
Urea (other names: Carbamid or E927b) is a natural metabolic product of mammals and is an important part of the nitrogen circle. On an industrial scale urea is produced from ammoniak.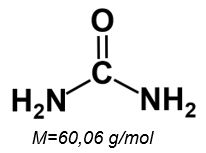 Urea is highly soluble in water. The analysis of urea with capillary electrophoresis is possible due to its affinity to micelles. Allthough it iss mall, it is sufficient to separate urea from the EOF. Detection takes place at low wave lengths with direct UV detection.
Urea is highly soluble in water. The analysis of urea with capillary electrophoresis is possible due to its affinity to micelles. Allthough it iss mall, it is sufficient to separate urea from the EOF. Detection takes place at low wave lengths with direct UV detection.
- Separation: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borate/SDS
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 10 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The linearity for the quantitation of urea was tested in the range of 20 mg/l up to 1000 mg/l.
Download: urea-linearity.pdf
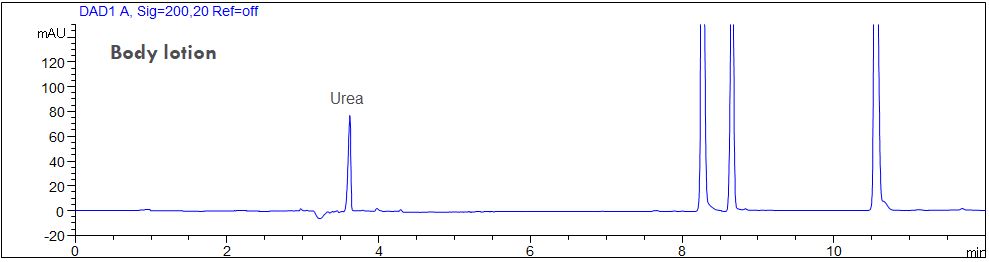
- Description: The amount of urea was determined in a body lotion and a pharmaceutical ointment for dry skins as described in the method above. The samples were extracted with pure water and injected instantly.
Download: urea1.pdf
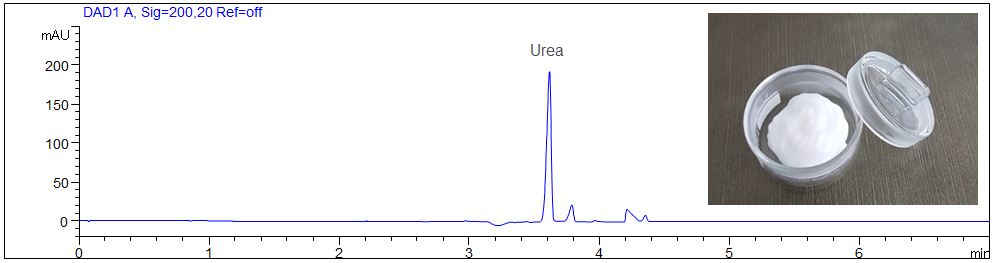
- Description: The hand cream was extracted with pure water and examined for urea.
Download: urea2.pdf
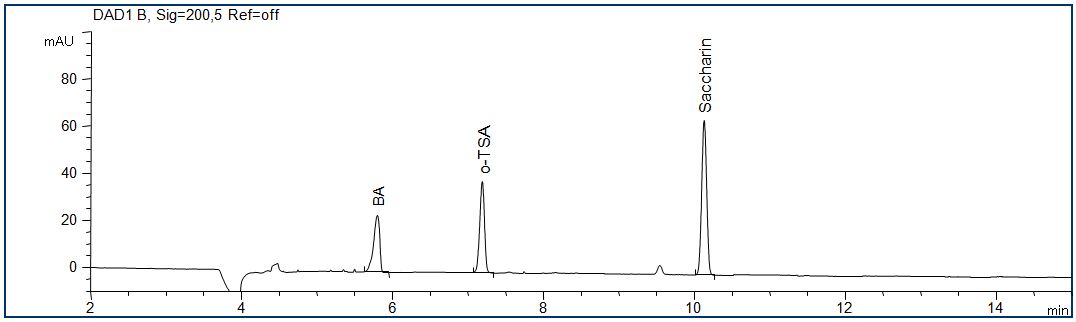
Benzamide, o-toluenesulfonic acid (o-TSA) und saccharin
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Borate/SDS
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, bubble cell, 64 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: The standard solution contains 10 mg/l benzamide, o-toluenesulfonic acid (o-TSA) and saccharin, each. Similar mixtures as used for industrial cleaning.
Download: Reinigungslösung.pdf
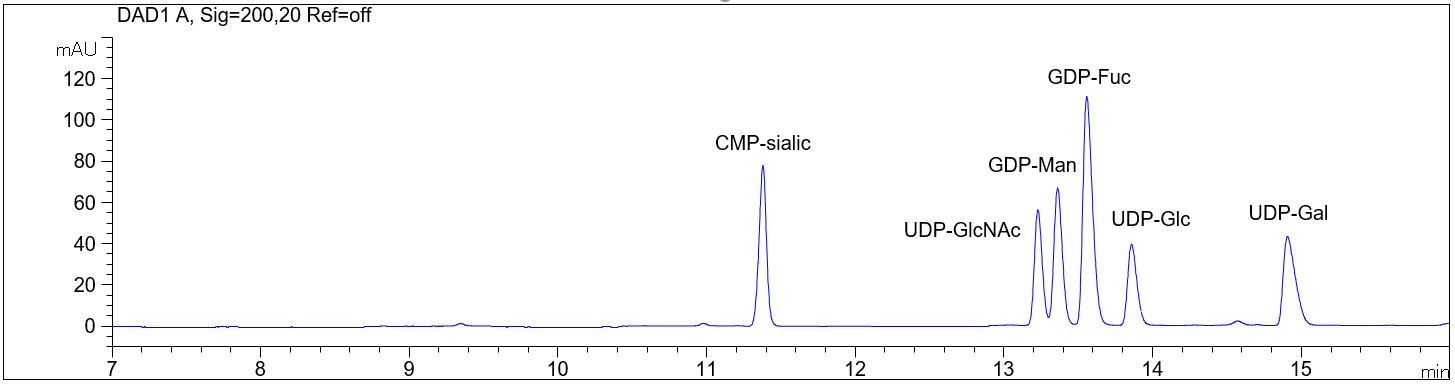
Nucleotide sugars
- Mode: CZE
- Electrolyte: Borate
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64 cm total
- Injection: hydrodynamic
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: Nucleotide sugars can be analyzed using a Borate electrolyte. The PDF shows the separation of the six nucleotide sugars: CMP-sialic (CAS 3063-71-6),UDP-GlcNAc (CAS 91183-98-1), GDP-Man (103301-73-1), GDP-Fuc (15839-70-0), UDP-Glc and UDP-Gal (CAS 137868-52-1). This method can be used for the determination of nucleotide sugars in cells.
Download: nucleotide-sugars.pdf
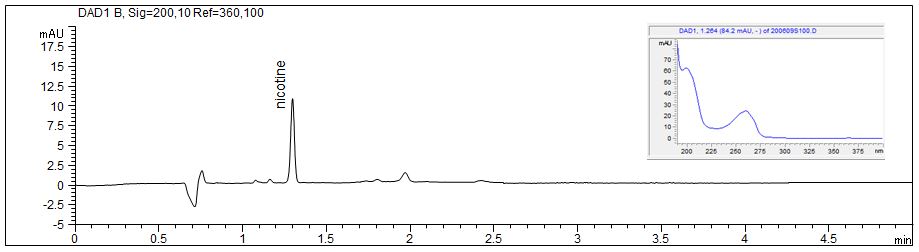
Nicotine
- Mode: MEKC
- Electrolyte: Borate and SDS
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64 cm total
- Injection: hydrodynamic
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm
- Description: Nicotine (C10H14N2; CAS: 54-11-5) can be analyzed using an electrolyte containing SDS. The PDF shows the spectral data and the calibration of nicotine.
Download: nicotine-1.pdf
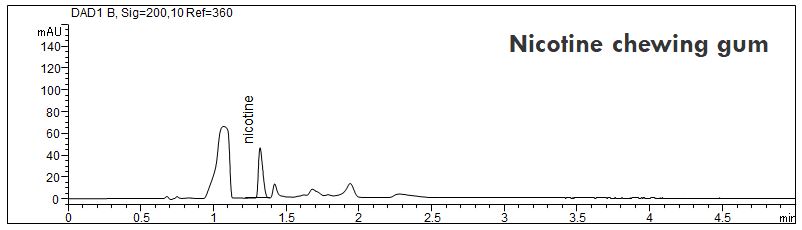
- Description: Nicotine (C10H14N2; CAS: 54-11-5) can be analyzed in various matrices. Sample preparation is done only by extraction using ethanol. The PDF shows the determination of nicotine in chewing gum, patches, tobacco and a solution of an E-cigarette.
Download: nicotine-2.pdf