Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) using direct UV-detection
EDTA is the tetraanion of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (CAS Number: 60-00-4). It can also be formed from different sodium salts like disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate (CAS Number: 6381-92-6). The pKa values of free EDTA are 0, 1.5, 2 and 2.66 (deprotonation of the four carboxyl groups) as well as 6.16 and 10.24 (deprotonation of the two amino groups).
Due to its complexing property there is a broad applicability for EDTA as preservatives in food or cosmetic products. Medical uses are the treatment of heavy metal (specifically Pb and Hg) intoxications and as anticoagulant in blood banks. Dentists need EDTA before the application of dental adhesives and in root canal therapy. Even eye drops contain EDTA to remove calcium deposits from the eye. Industrial and Household products like soaps contain EDTA mainly for the complexation of calcium and magnesium found in hard water. It is also included in mouthwashes and cosmetics.
Synonyms for EDTA are Titripex III, Edathamil, Edetate disodium salt dihydrate, Sequestrene Na2 and ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic acid disodium salt.
Due to its good solubility in water and its high charge (EDTA4−) it can be determined with Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. The carboxyl and the amino groups are able to form strong so called chelating complexes with bivalent metallic cations like copper.
- Separation modus: CZE
- Electrolyte: Borate
- Capillary: Bubble Cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, effective length: 8 cm
- Injection: hydrodynamic
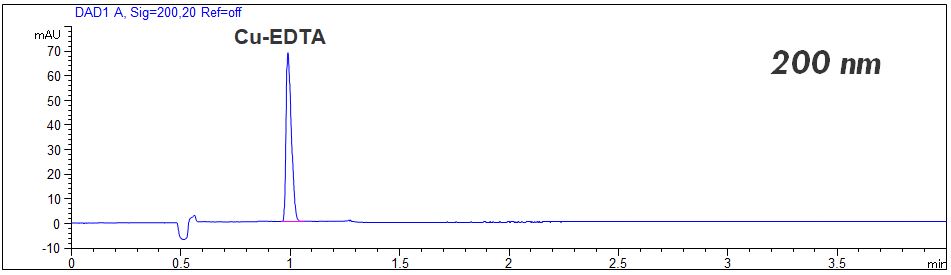
- Detection: direct UV, 200 nm or 260 nm
- Description: The free EDTA can be detected at 200 nm. For quantitation a quadratic regression is necessary. The complex of Cu-EDTA can be detected at 200 nm or at 260 nm. For quantitation of the Cu-EDTA complex a common linear regression is possible. Better limit of detection (LOD) can be achieved for the complexed EDTA. In the PDF the standard solutions of free EDTA and complexed EDTA are shown.
Download: Determination of free and complexed EDTA
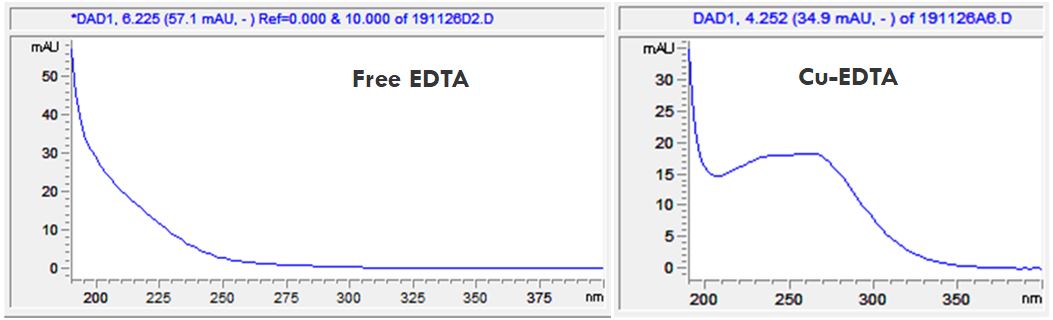
- Description: The different EDTA-metal complexes can be distinguished from each other with the help of their different spectral data. In the PDF the spectral data of the free EDTA and its Copper, Ferrum-, Magnesium and Calcium-complexes can be seen.
Download: Spectral data of EDTA
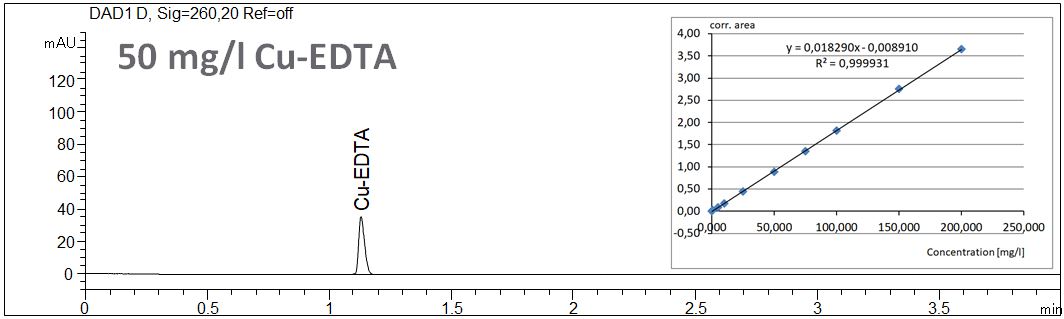
- Description: The linearity of the EDTA concentration using short end dection of copper complexes of EDTA is shown. In the PDF the statistical data of the linearity are summarized.
Download: Linearity of the determination of the EDTA-copper complexes
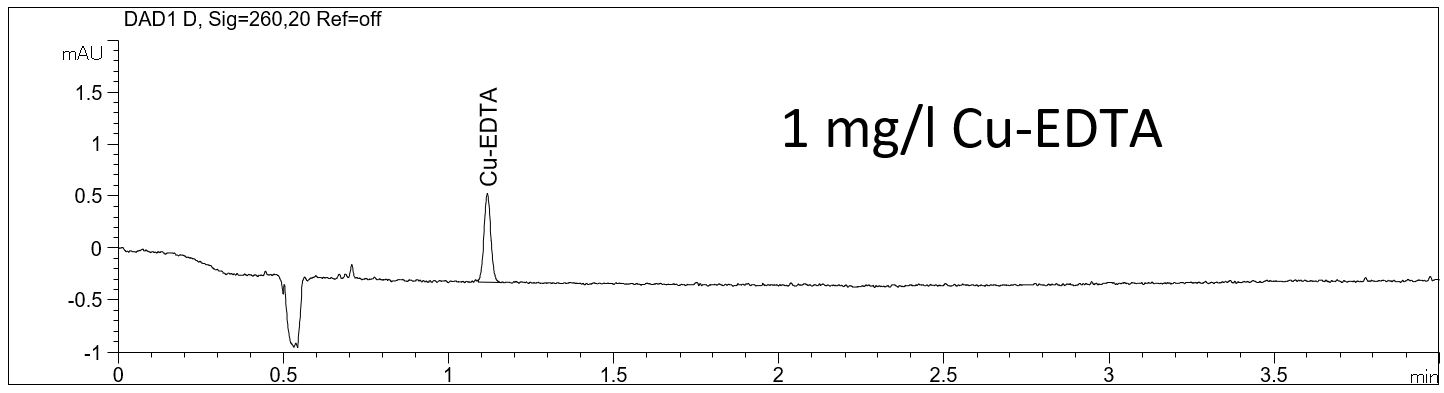
LOD of the complexed EDTA
- Description: A very sensitive limit of detection (LOD) can be achieved for the complexed EDTA. In the PDF the electropherograms of 1 mg/l standard solutions and the calculated LOD can be seen.
Download: LOD of EDTA
EDTA in nose drops
- Description: The EDTA concentration in nose drops was investigated. The nose drops were diluted 1:10 with pure water. In the PDF the electropherograms at 200 nm and 260 nm can be seen.
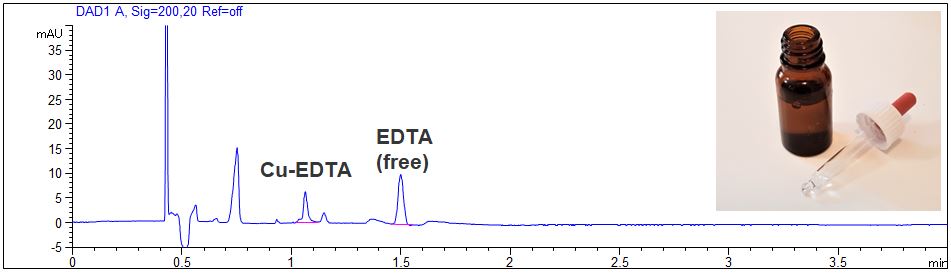
Determination of EDTA in nose drops
Download: EDTA in nose drops
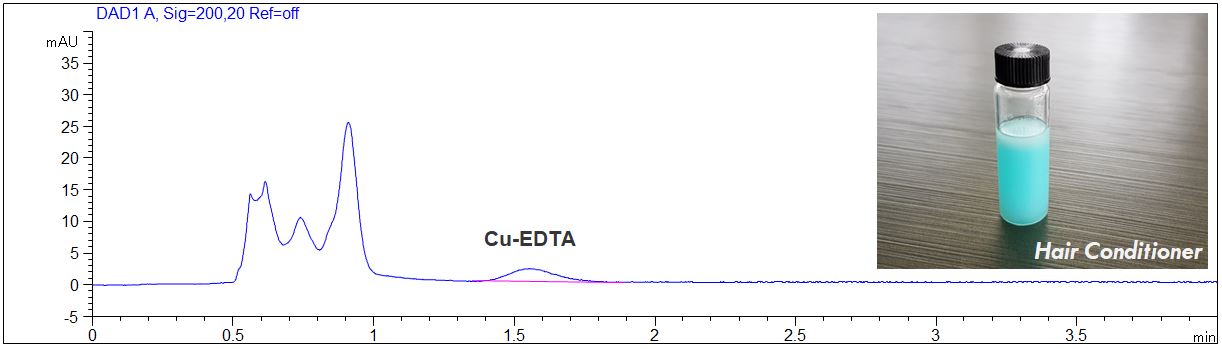
EDTA in Hair Conditioner
- Description: EDTA in Hair Conditioner was determined. The Hair Conditioner was diluted 1:10 with pure water. In the PDF the electropherograms of the Hair Conditioner and of a standard solution are shown.
Download: EDTA in Hair Conditioner