For the analysis of carbohydrates like glucose, fructose and sucrose with CE the charge and the detectability have to be optimized. Various CE methods have proven effective for this in practice: on the one hand it is possible to analyse carbohydrates at a high pH (12,1) with indirect UV detection. Under these conditions the carbohydrates are slightly dissociated anions. Unfortunately the resulting detectability is rather low.
Alternatively the samples could be derivatized for example with reductive amination using reagents like aminobenzene acidethylether (ABEE) and 6-aminochinoline (6-AQ). After the derivatization very good detectability and high selectivity can be achieved. The disadvantage of this procedure is the high effort for the sample preparation.
Eventually the carbohydrates can be analysed as anions in a high pH
(12,6) with direct UV detection. For this method a sample preparation is not necessary and the detectability is acceptable.
Hereafter examples for all three different methods are given.
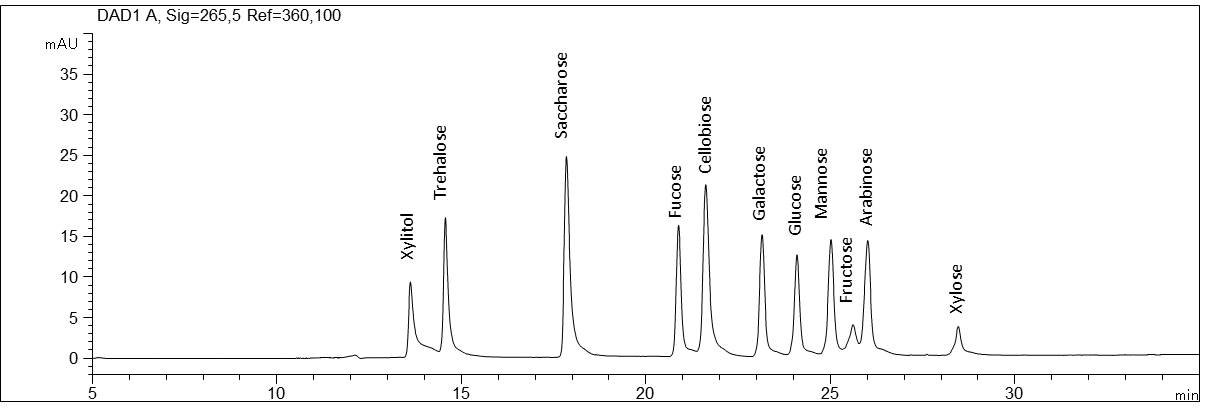
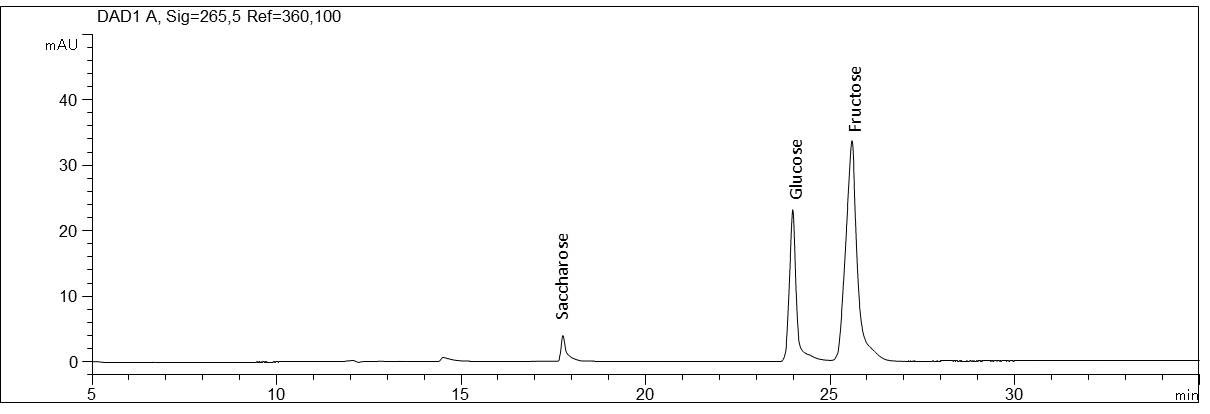
Carbohydrates with direct detection at a high pH value
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 12.6
- Capillary: Bubble cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 6 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 265 nm
- Description: The standard solution contains eleven different carbohydrates that can be analysed without sample pretreatment: Xylitol (E967, Pentapentol, birch sugar), trehalose (mykose), sucrose (cane sugar, beet sugar), fucose (methylpentose, desoxy galactose), cellobiose (cellose), galactose, glucose (dextrose), mannose, fructose (fruit sugar), arabinose (pectinose, aloin sugar) and xylose (wood sugar).
Download: Zucker_Standard.pdf
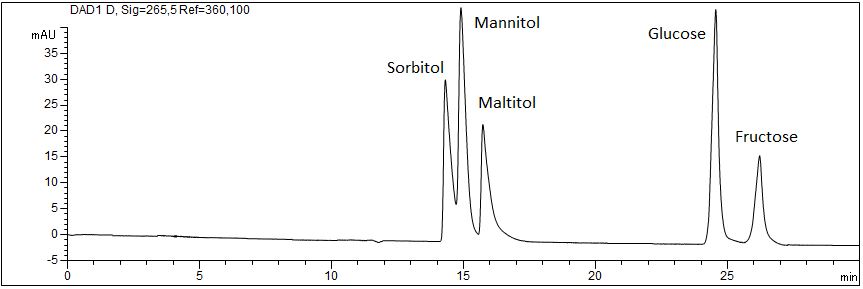
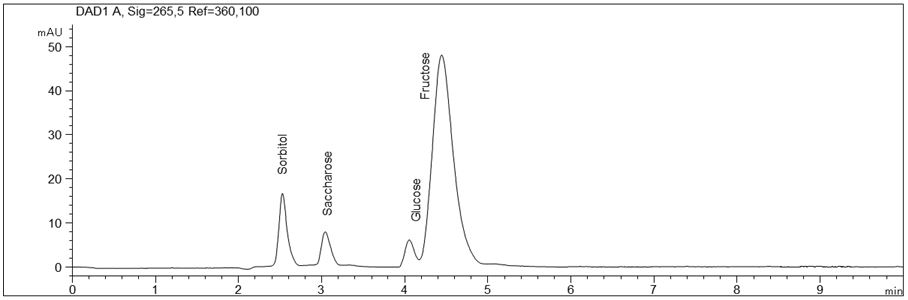
Analysis of sugar alcohols
Sugar alcohols have a sweet taste. As their metabolization is indepent of insulin they are widely used as sweeteners in many foods, especially sorbitol.
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 12.6
- Capillary: Bubble cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 6 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 265 nm
- Description: The standard solution contains sorbitol (E420), mannitol (E421, D-mannite), maltitol (E965, maltit) as well as glucose (dextrose) and fructose (fruit sugar) in a concentration of 500 mg/l each.
Download: Zuckeralkohole
Carbohydrates in strawberries
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 12.6
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 56 cm effective length, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 3 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 265 nm
- Description: In the PDF (402 KB) the e-grams and results of the analysis of carbohydates in eight sorts of strawberries are shown. The main sugars in strawberries are glucose and fructose. Sucrose was found only at low concentrations or not at all.
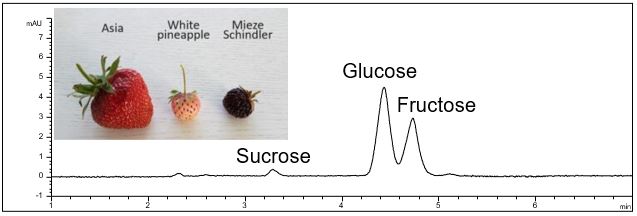
Carbohydrates in strawberries
Download (402 KB): Carbohydrates in eight sorts of strowberries: strawberries-carbohydrates
Carbohydrates in fruits
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 12.6
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 56 cm effective length, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 3 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 265 nm
- Description: In the PDF (334 KB) the e-grams of a short CE screening method for carbohydrates in a standard solution and in banana and strawberries are shown. The standard solution contains the following analytes: sucrose, glucose and fructose. It is evident, that glucose and fructose can be found in all fruits, but the concentration of sucrose differs.
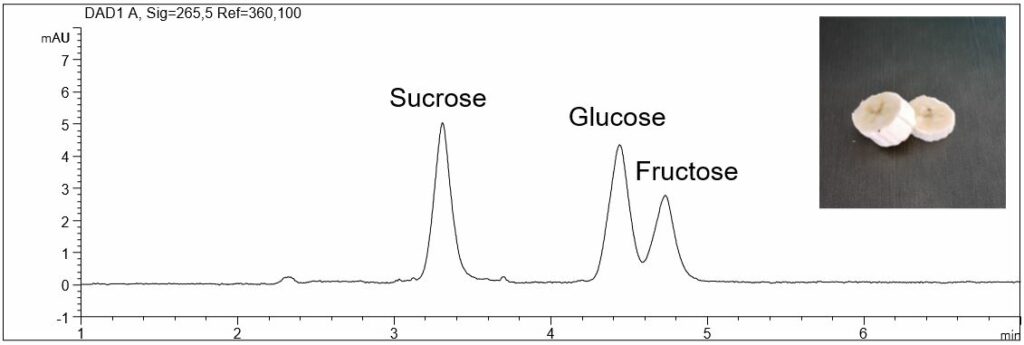
Carbohydrates in fruits (banana, strawberries)
Download: carbohydrates-fruits
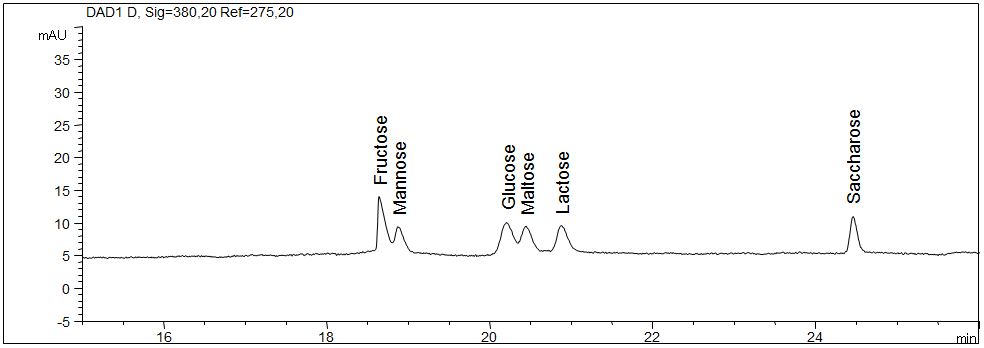
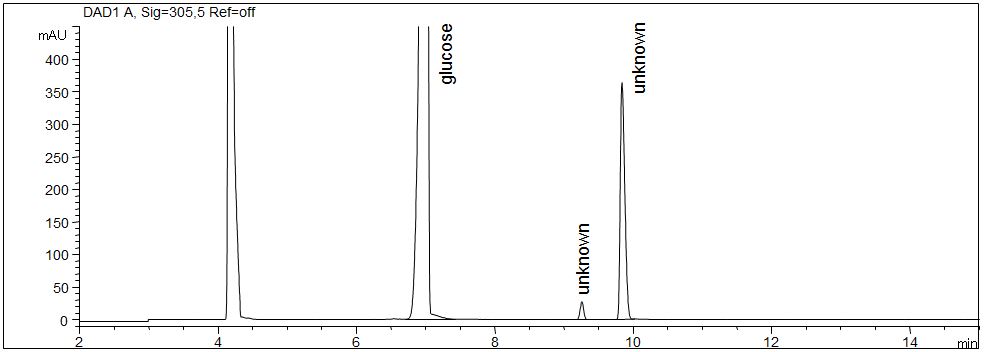
Carbohydrates with indirect detection
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Basic anion buffer, pH 12.1
- Capillary: fused silica, 50 µm ID, 114 cm in total
- Injection: 40 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: indirect UV, 275 nm
- Description: The standard solution contains six different carbohydrates: fructose (fruit sugar), mannose (niacinamide, vitamin PP), glucose (dextrose), maltose (malt sugar, maltobiose), lactose (milk sugar, lactobiose) and sucrose (cane sugar, beet sugar) in a concentration of 200 mg/l each. The EOF was reversed using a modifier in the electrolyte.
Download: Zucker_1.pdf
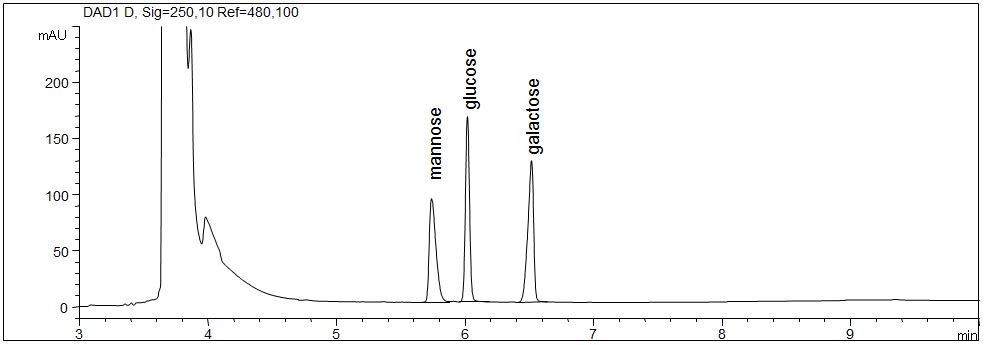
Carbohydrates after derivatization
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Borate
- Capillary: Bubble cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 48 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 250 nm
- Description: The standard solution with mannose (niacinamide, vitamin PP), glucose (dextrose) and galactose was derivatized with 6-aminochinoline before the determination.
Download: Zucker_2.pdf
Carbohydrates in fermentation broth after derivatization
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Borate
- Capillary: Bubble cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 48 cm in total
- Injection: 20 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 250 nm
- Description: Before the determination the fermentation broth was derivatized with 6-aminochinoline. Glucose could be identified and quantified and two other unidentified carbohydrates were determined.
Download: Zucker_3.pdf
Determination of sugars in different foods
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 12.6
- Capillary: Bubble cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 6 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 265 nm
- Description: The PDF shows electropherograms of eleven foods like drinks, fruit, vegetables and sausage.
Download: Zucker_Anwendungen.pdf
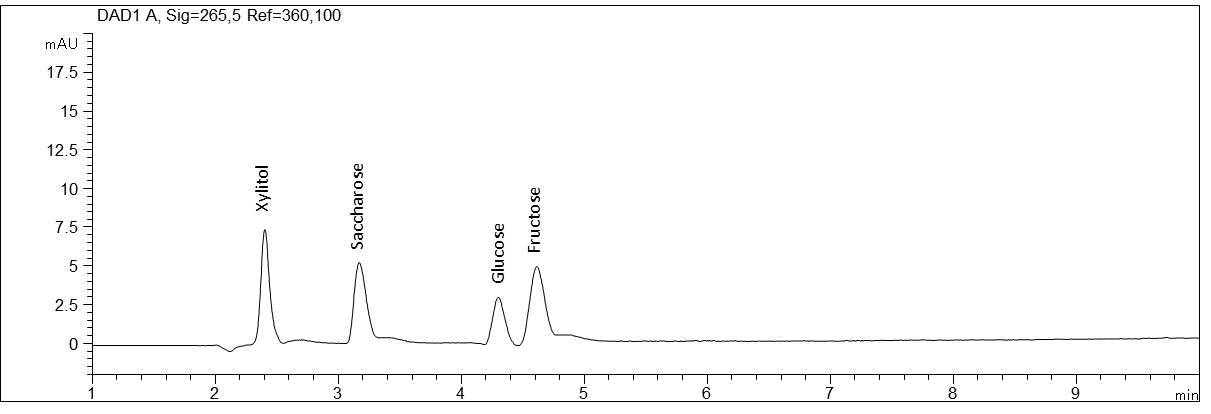
Determination of sugars with a fast screening method
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 12.6
- Capillary: Bubble cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 6 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 265 nm
- Description: All sugars relevant for the determination in foods can also be determined with the fast screening method. The anaylsis of Xylitol (E967, Pentapentol, birch sugar), sucrose (cane sugar, beet sugar), glucose (dextrose), mannose and fructose (fruit sugar) is successful in less than 10 min.
Download: Zucker_Standard_Screening.pdf
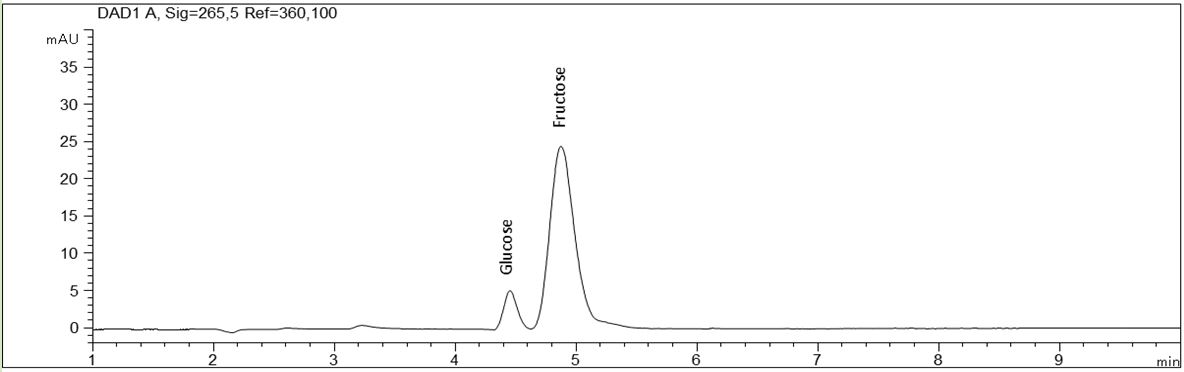
Determination of sugars in beverages with a fast screening method.
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 12.6
- Capillary: Bubble cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 6 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 265 nm
- Description: The PDF shows the analysis of glucose, fructose and sucrose with CE in
Download: Zucker-Saft-Prosecco.pdf
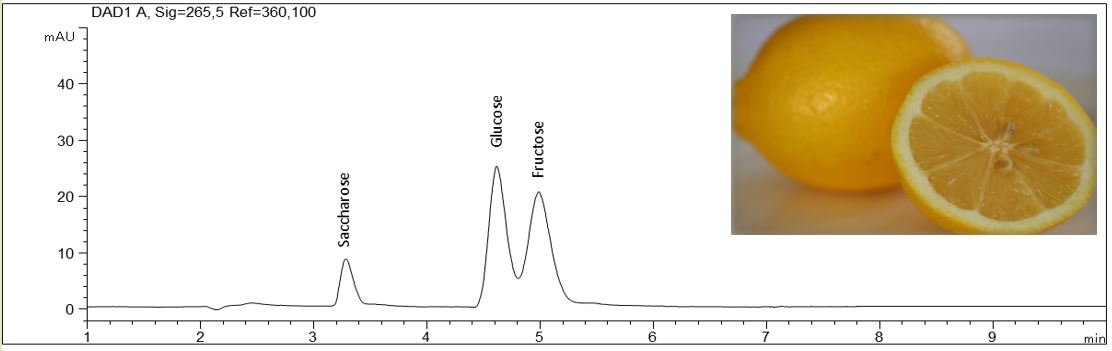
Determination of sugars in fruit with a fast screening method.
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 12.6
- Capillary: Bubble cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 6 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 265 nm
- Description: The five-sided PDF shows the analysis of glucose, fructose, sucrose, xylitol and sorbitol with CE in several fruits like lemon, pear and raspberries. For sample preparation the fruits were pureed, weighted and diluted with pure water.
Download: Zucker-Screening-Obst.pdf
Determination of sugars in foods with a fast screening method.
- Separation: CZE
- Electrolyte: Phosphate, pH 12.6
- Capillary: Bubble cell, fused silica, 50 µm ID, 64.5 cm in total
- Injection: 6 s, 50 mbar
- Detection: direct UV, 265 nm
- Description: All sugars relevant for the determination in foods can be determined with the fast screening method. The analysis of sorbitol (E420), sucrose (cane sugar, beet sugar), glucose (dextrose) and fructose (fruit sugar) is successful in less than 10 min. In total 16 electropherograms are shown of beverages, vegetable and tooth paste for children.
Download: Zucker_Anwendungen_Screening